0 attempts
0% avg
| Step | Derivation/Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \[ F_\text{output} = mg \] | Calculate the force due to the mass of the rock. Here, \( m = 55.2 \, \text{kg} \) and \( g = 9.81 \, \text{m/s}^2 \). |
| 2 | \[ F_\text{output} = 55.2 \times 9.81 \] | Substitute values to find the force on the output plunger. |
| 3 | \[ F_\text{output} = 541.212 \, \text{N} \] | The force exerted by the rock on the output plunger. |
| 4 | \[ \frac{F_\text{input}}{A_\text{input}} = \frac{F_\text{output}}{A_\text{output}} \] | Use Pascal’s principle, which states that pressure is transmitted undiminished in an enclosed static fluid. |
| 5 | \[ F_\text{input} = \frac{F_\text{output} \times A_\text{input}}{A_\text{output}} \] | Rearrange to solve for the input force needed for equilibrium. |
| 6 | \[ F_\text{input} = \frac{541.212 \times 15}{65} \] | Substitute the area values: \( A_\text{input} = 15 \, \text{cm}^2 \) and \( A_\text{output} = 65 \, \text{cm}^2 \). |
| 7 | \[ F_\text{input} = 124.843 \, \text{N} \] | Calculate the force exerted on the input piston necessary for equilibrium. |
| 8 | \[ 124.843 = k_s \Delta x \] | Relate the input force to the spring constant \( k_s = 1250 \, \text{N/m} \) and the compression \( \Delta x \). |
| 9 | \[ \Delta x = \frac{124.843}{1250} \] | Solve for the compression of the spring. |
| 10 | \[ \Delta x = 0.0999 \, \text{m} \] | Convert the compression to meters. |
| 11 | \[ \boxed{9.99 \, \text{cm}} \] | Convert to centimeters and box the final answer. |
| Step | Derivation/Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \[ A_\text{input} \Delta y_\text{input} = A_\text{output} \Delta y_\text{output} \] | Use the principle of conservation of volume in the hydraulic system. |
| 2 | \[ 15 \times 22.0 = 65 \times \Delta y_\text{output} \] | Substitute \( \Delta y_\text{input} = 22.0 \, \text{cm} \) and the areas. |
| 3 | \[ 330 = 65 \times \Delta y_\text{output} \] | Calculate the product of the input area and the distance. |
| 4 | \[ \Delta y_\text{output} = \frac{330}{65} \] | Solve for the rise in the output plunger’s height. |
| 5 | \[ \Delta y_\text{output} = 5.077 \, \text{cm} \] | The final rise in the output plunger. |
| 6 | \[ \boxed{5.08 \, \text{cm}} \] | Box the final answer after rounding to two decimal places. |
| Step | Derivation/Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \[ P = P_0 + \rho g h \] | The absolute pressure at a depth \( h \) is given by this equation, where \( P_0 \) is atmospheric pressure. |
| 2 | \[ P = 101325 + 1000 \times 9.81 \times 0.85 \] | Substitute \( P_0 = 101325 \, \text{Pa} \), \( \rho = 1000 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \), \( g = 9.81 \, \text{m/s}^2 \), and the height \( h = 0.85 \, \text{m} \). |
| 3 | \[ P = 101325 + 8338.5 \] | Calculate the pressure contribution from the water column. |
| 4 | \[ P = 109663.5 \, \text{Pa} \] | Calculate the total absolute pressure at the bottom of the chamber. |
| 5 | \[ \boxed{109664 \, \text{Pa}} \] | Box the final answer after rounding to the nearest Pascal. |
Just ask: "Help me solve this problem."
We'll help clarify entire units in one hour or less — guaranteed.
Two objects labeled K and L have equal mass but densities \( 0.95D_o \) and \( D_o \), respectively. Each of these objects floats after being thrown into a deep swimming pool. Which is true about the buoyant forces acting on these objects?
Balsa wood with an average density of \( 130 \) \( \text{kg/m}^3 \), is floating in pure water. What percentage of the wood is submerged?
An ideal fluid flows through a pipe with radius \( Q \) and flow speed \( V \). If the pipe splits up into three separate paths, each with radius \( \frac{Q}{2} \), what is the flow speed through each of the paths?
A spherical balloon has a radius of \(7.15\) \(\text{m}\) and is filled with helium. How large a cargo can it lift, assuming that the skin and structure of the balloon have a mass of \(930\) \(\text{kg}\)?
Take the density of helium and air to be \(0.18\) \(\text{kg/m}^3\) and \(1.24\) \(\text{kg/m}^3\), respectively.
How large must a heating duct be if air moving \( 3 \ \frac{\text{m}}{\text{s}} \) along it can replenish the air in a room of \( 300 \ \text{m}^3 \) volume every \( 15 \) minutes? Assume the air’s density remains constant.
A trash compactor pushes down with a force of \( 500 \) \( \text{N} \) on a \( 3 \) \( \text{cm}^2 \) input piston, causing a force of \( 30,000 \) \( \text{N} \) to crush the trash. What is the area of the output piston that crushes the trash?

A horizontal tube with two vertical T-branches (A and B) is partially submerged in a liquid, with the open ends of the branches exposed to the air. However, the section of the tube above point B is hidden from view and may either be wider or narrower than the section above A.
Air is blown through the horizontal tube, causing the liquid levels in the vertical branches to rise as shown. Based on the observed water levels, which of the following best describes the characteristics of the hidden section of the tube above B?
Caleb is filling up water balloons for the Physics Olympics balloon toss competition. Caleb sets a \( 0.50 \text{-kg} \) spherical water balloon on the kitchen table and notices that the bottom of the balloon flattens until the pressure on the bottom is reduced to \( 630 \frac{\text{N}}{\text{m}^2} \). What is the area of the flat spot on the bottom of the balloon?
A fountain with an opening of radius \( 0.015 \) \( \text{m} \) shoots a stream of water vertically from ground level at \( 6.0 \) \( \text{m/s} \). The density of water is \( 1000 \) \( \text{kg/m}^3 \).
A small rock sits at the bottom of a cup filled with water. The upward force exerted by the water on the rock is \( F_0 \). The water is then poured out and replaced by an oil that is \( \frac{3}{4} \) as dense as water, and the rock again sits at the bottom of the cup, completely under the oil. Which of the following expressions correctly represents the magnitude of the upward force exerted by the oil on the rock?
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
| Kinematics | Forces |
|---|---|
| \(\Delta x = v_i t + \frac{1}{2} at^2\) | \(F = ma\) |
| \(v = v_i + at\) | \(F_g = \frac{G m_1 m_2}{r^2}\) |
| \(v^2 = v_i^2 + 2a \Delta x\) | \(f = \mu N\) |
| \(\Delta x = \frac{v_i + v}{2} t\) | \(F_s =-kx\) |
| \(v^2 = v_f^2 \,-\, 2a \Delta x\) |
| Circular Motion | Energy |
|---|---|
| \(F_c = \frac{mv^2}{r}\) | \(KE = \frac{1}{2} mv^2\) |
| \(a_c = \frac{v^2}{r}\) | \(PE = mgh\) |
| \(T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{r}{g}}\) | \(KE_i + PE_i = KE_f + PE_f\) |
| \(W = Fd \cos\theta\) |
| Momentum | Torque and Rotations |
|---|---|
| \(p = mv\) | \(\tau = r \cdot F \cdot \sin(\theta)\) |
| \(J = \Delta p\) | \(I = \sum mr^2\) |
| \(p_i = p_f\) | \(L = I \cdot \omega\) |
| Simple Harmonic Motion | Fluids |
|---|---|
| \(F = -kx\) | \(P = \frac{F}{A}\) |
| \(T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{l}{g}}\) | \(P_{\text{total}} = P_{\text{atm}} + \rho gh\) |
| \(T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}\) | \(Q = Av\) |
| \(x(t) = A \cos(\omega t + \phi)\) | \(F_b = \rho V g\) |
| \(a = -\omega^2 x\) | \(A_1v_1 = A_2v_2\) |
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| [katex]g[/katex] | Acceleration due to gravity, typically [katex]9.8 , \text{m/s}^2[/katex] on Earth’s surface |
| [katex]G[/katex] | Universal Gravitational Constant, [katex]6.674 \times 10^{-11} , \text{N} \cdot \text{m}^2/\text{kg}^2[/katex] |
| [katex]\mu_k[/katex] and [katex]\mu_s[/katex] | Coefficients of kinetic ([katex]\mu_k[/katex]) and static ([katex]\mu_s[/katex]) friction, dimensionless. Static friction ([katex]\mu_s[/katex]) is usually greater than kinetic friction ([katex]\mu_k[/katex]) as it resists the start of motion. |
| [katex]k[/katex] | Spring constant, in [katex]\text{N/m}[/katex] |
| [katex] M_E = 5.972 \times 10^{24} , \text{kg} [/katex] | Mass of the Earth |
| [katex] M_M = 7.348 \times 10^{22} , \text{kg} [/katex] | Mass of the Moon |
| [katex] M_M = 1.989 \times 10^{30} , \text{kg} [/katex] | Mass of the Sun |
| Variable | SI Unit |
|---|---|
| [katex]s[/katex] (Displacement) | [katex]\text{meters (m)}[/katex] |
| [katex]v[/katex] (Velocity) | [katex]\text{meters per second (m/s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]a[/katex] (Acceleration) | [katex]\text{meters per second squared (m/s}^2\text{)}[/katex] |
| [katex]t[/katex] (Time) | [katex]\text{seconds (s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]m[/katex] (Mass) | [katex]\text{kilograms (kg)}[/katex] |
| Variable | Derived SI Unit |
|---|---|
| [katex]F[/katex] (Force) | [katex]\text{newtons (N)}[/katex] |
| [katex]E[/katex], [katex]PE[/katex], [katex]KE[/katex] (Energy, Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy) | [katex]\text{joules (J)}[/katex] |
| [katex]P[/katex] (Power) | [katex]\text{watts (W)}[/katex] |
| [katex]p[/katex] (Momentum) | [katex]\text{kilogram meters per second (kgm/s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]\omega[/katex] (Angular Velocity) | [katex]\text{radians per second (rad/s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]\tau[/katex] (Torque) | [katex]\text{newton meters (Nm)}[/katex] |
| [katex]I[/katex] (Moment of Inertia) | [katex]\text{kilogram meter squared (kgm}^2\text{)}[/katex] |
| [katex]f[/katex] (Frequency) | [katex]\text{hertz (Hz)}[/katex] |
Metric Prefixes
Example of using unit analysis: Convert 5 kilometers to millimeters.
Start with the given measurement: [katex]\text{5 km}[/katex]
Use the conversion factors for kilometers to meters and meters to millimeters: [katex]\text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}}[/katex]
Perform the multiplication: [katex]\text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}} = 5 \times 10^3 \times 10^3 \, \text{mm}[/katex]
Simplify to get the final answer: [katex]\boxed{5 \times 10^6 \, \text{mm}}[/katex]
Prefix | Symbol | Power of Ten | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
Pico- | p | [katex]10^{-12}[/katex] | 0.000000000001 |
Nano- | n | [katex]10^{-9}[/katex] | 0.000000001 |
Micro- | µ | [katex]10^{-6}[/katex] | 0.000001 |
Milli- | m | [katex]10^{-3}[/katex] | 0.001 |
Centi- | c | [katex]10^{-2}[/katex] | 0.01 |
Deci- | d | [katex]10^{-1}[/katex] | 0.1 |
(Base unit) | – | [katex]10^{0}[/katex] | 1 |
Deca- or Deka- | da | [katex]10^{1}[/katex] | 10 |
Hecto- | h | [katex]10^{2}[/katex] | 100 |
Kilo- | k | [katex]10^{3}[/katex] | 1,000 |
Mega- | M | [katex]10^{6}[/katex] | 1,000,000 |
Giga- | G | [katex]10^{9}[/katex] | 1,000,000,000 |
Tera- | T | [katex]10^{12}[/katex] | 1,000,000,000,000 |
One price to unlock most advanced version of Phy across all our tools.
per month
Billed Monthly. Cancel Anytime.
We crafted THE Ultimate A.P Physics 1 Program so you can learn faster and score higher.
Try our free calculator to see what you need to get a 5 on the 2026 AP Physics 1 exam.
A quick explanation
Credits are used to grade your FRQs and GQs. Pro users get unlimited credits.
Submitting counts as 1 attempt.
Viewing answers or explanations count as a failed attempts.
Phy gives partial credit if needed
MCQs and GQs are are 1 point each. FRQs will state points for each part.
Phy customizes problem explanations based on what you struggle with. Just hit the explanation button to see.
Understand you mistakes quicker.
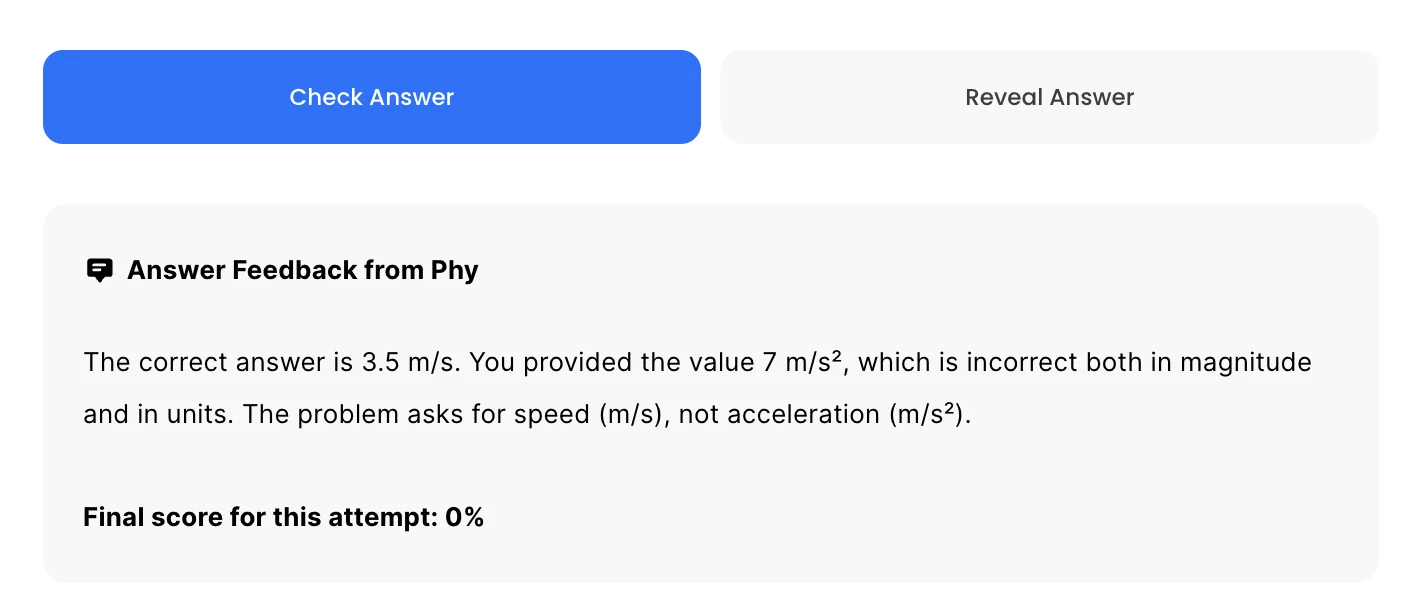
Phy automatically provides feedback so you can improve your responses.
10 Free Credits To Get You Started
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.
Feeling uneasy about your next physics test? We'll boost your grade in 3 lessons or less—guaranteed
NEW! PHY AI accurately solves all questions
🔥 Get up to 30% off Elite Physics Tutoring
🧠 NEW! Learn Physics From Scratch Self Paced Course
🎯 Need exam style practice questions?