0 attempts
0% avg
| Step | Derivation or Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \[K_i = \frac{1}{2} m v_i^2\] | The box begins with kinetic energy \(K_i\). |
| 2 | \[W_s = K_f – K_i\] | The spring’s work \(W_s\) equals the change in kinetic energy \(\Delta K\). |
| 3 | \[K_f = 0\] | At maximum compression the box momentarily stops, so \(K_f = 0\). |
| 4 | \[W_s = -K_i\] | Since \(K_i > 0\) and \(K_f = 0\), the spring does negative work (it removes energy from the box). |
| Step | Derivation or Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \[K_i = \frac{1}{2}(20)(4.0)^2 = 160\,\text{J}\] | Compute the initial kinetic energy using \(m = 20\,\text{kg}\) and \(v_i = 4.0\,\text{m/s}\). |
| 2 | \[|W_s| = K_i = 160\,\text{J}\] | The magnitude of the spring’s work equals the lost kinetic energy. |
| Step | Derivation or Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \[W_s = -\frac{1}{2}k x_{\max}^2\] | Work done by a spring compressing from \(0\) to \(x_{\max}\). |
| 2 | \[-160 = -\frac{1}{2}k(0.50)^2\] | Insert \(|W_s| = 160\,\text{J}\) and \(x_{\max} = 0.50\,\text{m}\). |
| 3 | \[k = 1.28 \times 10^3\,\text{N/m}\] | Solve for the spring constant. |
| Step | Derivation or Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \[a_{\max} = \frac{k x_{\max}}{m}\] | For simple harmonic motion, acceleration magnitude is \(|a| = (k/m)|x|\); maximum occurs at amplitude. |
| 2 | \[a_{\max} = \frac{(1.28\times10^3)(0.50)}{20} = 32\,\text{m/s}^2\] | Substitute \(k\), \(x_{\max}\), and \(m\). |
| Step | Derivation or Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \[f = \frac{1}{2\pi}\sqrt{\frac{k}{m}}\] | Frequency of a mass–spring system on a frictionless surface. |
| 2 | \[f = \frac{1}{2\pi}\sqrt{\frac{1.28\times10^3}{20}} \approx 1.27\,\text{Hz}\] | Insert \(k\) and \(m\) and simplify. |
| Step | Derivation or Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | \[E = \frac{1}{2}kA^2 = 160\,\text{J}\] | Total mechanical energy \(E\) equals the initial kinetic energy; amplitude \(A = 0.50\,\text{m}\). |
| 2 | \[K(x) = E – \frac{1}{2}k x^2 = 160 – 640 x^2\] | Kinetic energy as a function of position for simple harmonic motion. |
| 3 | \[K(\pm0.50) = 0,\; K(0)=160\,\text{J}\] | Shows the endpoints and midpoint values used for sketching. |
| 4 | \[\text{Parabolic}\] | The graph is an inverted parabola opening downward, symmetric about \(x=0\), peaking at \(160\,\text{J}\) and touching the horizontal axis at \(x = \pm0.50\,\text{m}\). |
Just ask: "Help me solve this problem."
We'll help clarify entire units in one hour or less — guaranteed.

A sphere starts from rest and rolls down an incline of height \( H = 1.0 \) \( \text{m} \) at an angle of \( 25^\circ \) with the horizontal, as shown above. The radius of the sphere \( R = 15 \) \( \text{cm} \), and its mass \( m = 1.0 \) \( \text{kg} \). The moment of inertia for a sphere is \( \frac{2}{5}mR^2 \). What is the speed of the sphere when it reaches the bottom of the plane?
A spring stretches \( 8.0 \) \( \text{cm} \) when a \( 13 \) \( \text{N} \) force is applied. How far does it stretch when a \( 26 \) \( \text{N} \) force is applied?
A net force of \( 8.0 \) \( \text{N} \) accelerates a \( 4.0 \) \( \text{kg} \) body from rest to a speed of \( 5.0 \) \( \text{m s}^{-1} \). Which of the following is equal to the work done by the force?
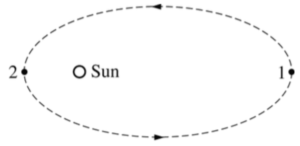
The elliptical orbit of a comet is shown above. Positions 1 and 2 are, respectively, the farthest and nearest positions to the Sun, and at position 1 the distance from the comet to the Sun is 10 times that at position 2. At position 2, the comet’s kinetic energy is
A horizontal force of \(110 \, \text{N}\) is applied to a \(12 \, \text{kg}\) object, moving it \(6 \, \text{m}\) on a horizontal surface where the kinetic friction coefficient is \(\mu_k = 0.25\). The object then slides up a \(17^\circ\) inclined plane. Assuming the \(110 \, \text{N}\) force is no longer acting on the incline, and the coefficient of kinetic friction there is \(\mu_k = 0.45\), calculate the distance the object will slide on the incline.
The total energy of a system in SHM is given by \( E \). At what displacement from equilibrium is the kinetic energy equal to the potential energy?
A snowboarder starts from rest and slides down a \(32^\circ\) incline that’s \(75 \, \text{m}\) long.
A typical \( 68 \text{-kg} \) person generates a steady mechanical power output of \( 120 \text{ W} \) at the pedals of a bicycle. Approximately how many Calories are “burned” (total metabolic energy expended) when the person rides a bicycle for \( 15 \text{ minutes} \)? A typical energy efficiency for the human body is \( 25\% \), which takes into account the release of thermal energy. Note (\( 1 \text{ Cal} = 4186 \text{ J} \)).
A bullet at speed [katex] v_0 [/katex] trikes and embeds itself in a block of wood which is suspended by a string, causing the bullet and block to rise to a maximum height h. Which of the following statements is true?
It takes \(4 \, \text{s}\) for an individual to push a \(70 \, \text{kg}\) box up a \(5 \, \text{m}\) long, \(12^\circ\) ramp. The box starts from rest and achieves a speed of \(2.5 \, \text{m/s}\) at the top. Friction does \(350 \, \text{J}\) of work during its ascent. Calculate the power output of the individual pushing the box.
\(\text{Negative}\)
\(160\,\text{J}\)
\(1.28\times10^{3}\,\text{N/m}\)
\(32\,\text{m/s^{2}}\)
\(1.27\,\text{Hz}\)
\(K(x)=160-640x^{2}\)
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
| Kinematics | Forces |
|---|---|
| \(\Delta x = v_i t + \frac{1}{2} at^2\) | \(F = ma\) |
| \(v = v_i + at\) | \(F_g = \frac{G m_1 m_2}{r^2}\) |
| \(v^2 = v_i^2 + 2a \Delta x\) | \(f = \mu N\) |
| \(\Delta x = \frac{v_i + v}{2} t\) | \(F_s =-kx\) |
| \(v^2 = v_f^2 \,-\, 2a \Delta x\) |
| Circular Motion | Energy |
|---|---|
| \(F_c = \frac{mv^2}{r}\) | \(KE = \frac{1}{2} mv^2\) |
| \(a_c = \frac{v^2}{r}\) | \(PE = mgh\) |
| \(T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{r}{g}}\) | \(KE_i + PE_i = KE_f + PE_f\) |
| \(W = Fd \cos\theta\) |
| Momentum | Torque and Rotations |
|---|---|
| \(p = mv\) | \(\tau = r \cdot F \cdot \sin(\theta)\) |
| \(J = \Delta p\) | \(I = \sum mr^2\) |
| \(p_i = p_f\) | \(L = I \cdot \omega\) |
| Simple Harmonic Motion | Fluids |
|---|---|
| \(F = -kx\) | \(P = \frac{F}{A}\) |
| \(T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{l}{g}}\) | \(P_{\text{total}} = P_{\text{atm}} + \rho gh\) |
| \(T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}\) | \(Q = Av\) |
| \(x(t) = A \cos(\omega t + \phi)\) | \(F_b = \rho V g\) |
| \(a = -\omega^2 x\) | \(A_1v_1 = A_2v_2\) |
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| [katex]g[/katex] | Acceleration due to gravity, typically [katex]9.8 , \text{m/s}^2[/katex] on Earth’s surface |
| [katex]G[/katex] | Universal Gravitational Constant, [katex]6.674 \times 10^{-11} , \text{N} \cdot \text{m}^2/\text{kg}^2[/katex] |
| [katex]\mu_k[/katex] and [katex]\mu_s[/katex] | Coefficients of kinetic ([katex]\mu_k[/katex]) and static ([katex]\mu_s[/katex]) friction, dimensionless. Static friction ([katex]\mu_s[/katex]) is usually greater than kinetic friction ([katex]\mu_k[/katex]) as it resists the start of motion. |
| [katex]k[/katex] | Spring constant, in [katex]\text{N/m}[/katex] |
| [katex] M_E = 5.972 \times 10^{24} , \text{kg} [/katex] | Mass of the Earth |
| [katex] M_M = 7.348 \times 10^{22} , \text{kg} [/katex] | Mass of the Moon |
| [katex] M_M = 1.989 \times 10^{30} , \text{kg} [/katex] | Mass of the Sun |
| Variable | SI Unit |
|---|---|
| [katex]s[/katex] (Displacement) | [katex]\text{meters (m)}[/katex] |
| [katex]v[/katex] (Velocity) | [katex]\text{meters per second (m/s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]a[/katex] (Acceleration) | [katex]\text{meters per second squared (m/s}^2\text{)}[/katex] |
| [katex]t[/katex] (Time) | [katex]\text{seconds (s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]m[/katex] (Mass) | [katex]\text{kilograms (kg)}[/katex] |
| Variable | Derived SI Unit |
|---|---|
| [katex]F[/katex] (Force) | [katex]\text{newtons (N)}[/katex] |
| [katex]E[/katex], [katex]PE[/katex], [katex]KE[/katex] (Energy, Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy) | [katex]\text{joules (J)}[/katex] |
| [katex]P[/katex] (Power) | [katex]\text{watts (W)}[/katex] |
| [katex]p[/katex] (Momentum) | [katex]\text{kilogram meters per second (kgm/s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]\omega[/katex] (Angular Velocity) | [katex]\text{radians per second (rad/s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]\tau[/katex] (Torque) | [katex]\text{newton meters (Nm)}[/katex] |
| [katex]I[/katex] (Moment of Inertia) | [katex]\text{kilogram meter squared (kgm}^2\text{)}[/katex] |
| [katex]f[/katex] (Frequency) | [katex]\text{hertz (Hz)}[/katex] |
Metric Prefixes
Example of using unit analysis: Convert 5 kilometers to millimeters.
Start with the given measurement: [katex]\text{5 km}[/katex]
Use the conversion factors for kilometers to meters and meters to millimeters: [katex]\text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}}[/katex]
Perform the multiplication: [katex]\text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}} = 5 \times 10^3 \times 10^3 \, \text{mm}[/katex]
Simplify to get the final answer: [katex]\boxed{5 \times 10^6 \, \text{mm}}[/katex]
Prefix | Symbol | Power of Ten | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
Pico- | p | [katex]10^{-12}[/katex] | 0.000000000001 |
Nano- | n | [katex]10^{-9}[/katex] | 0.000000001 |
Micro- | µ | [katex]10^{-6}[/katex] | 0.000001 |
Milli- | m | [katex]10^{-3}[/katex] | 0.001 |
Centi- | c | [katex]10^{-2}[/katex] | 0.01 |
Deci- | d | [katex]10^{-1}[/katex] | 0.1 |
(Base unit) | – | [katex]10^{0}[/katex] | 1 |
Deca- or Deka- | da | [katex]10^{1}[/katex] | 10 |
Hecto- | h | [katex]10^{2}[/katex] | 100 |
Kilo- | k | [katex]10^{3}[/katex] | 1,000 |
Mega- | M | [katex]10^{6}[/katex] | 1,000,000 |
Giga- | G | [katex]10^{9}[/katex] | 1,000,000,000 |
Tera- | T | [katex]10^{12}[/katex] | 1,000,000,000,000 |
One price to unlock most advanced version of Phy across all our tools.
per month
Billed Monthly. Cancel Anytime.
We crafted THE Ultimate A.P Physics 1 Program so you can learn faster and score higher.
Try our free calculator to see what you need to get a 5 on the 2026 AP Physics 1 exam.
A quick explanation
Credits are used to grade your FRQs and GQs. Pro users get unlimited credits.
Submitting counts as 1 attempt.
Viewing answers or explanations count as a failed attempts.
Phy gives partial credit if needed
MCQs and GQs are are 1 point each. FRQs will state points for each part.
Phy customizes problem explanations based on what you struggle with. Just hit the explanation button to see.
Understand you mistakes quicker.
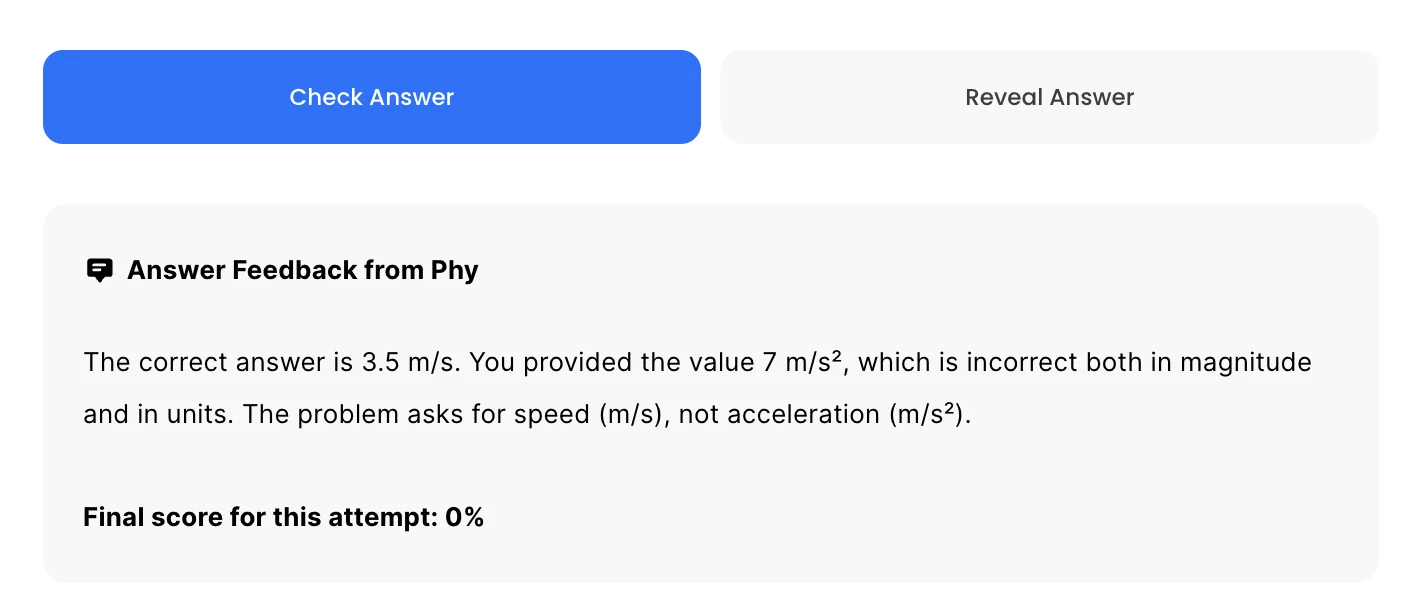
Phy automatically provides feedback so you can improve your responses.
10 Free Credits To Get You Started
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.
Feeling uneasy about your next physics test? We'll boost your grade in 3 lessons or less—guaranteed
NEW! PHY AI accurately solves all questions
🔥 Get up to 30% off Elite Physics Tutoring
🧠 NEW! Learn Physics From Scratch Self Paced Course
🎯 Need exam style practice questions?