0 attempts
0% avg
UBQ Credits
| Step | Derivation/Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [katex]F = ma[/katex] | The net force acting on each vehicle due to friction is equal to the mass of the vehicle times its acceleration (Newton’s Second Law). |
| 2 | [katex]a = \frac{F}{m}[/katex] | Acceleration [katex] a [/katex] can be expressed as the force divided by the mass. Given that [katex] F [/katex] is the same for both, the acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass. |
| 3 | [katex]v_f = v_i + at[/katex] | The final velocity [katex]v_f[/katex] of each vehicle can be found using the kinematic equation where [katex]v_i[/katex] is the initial velocity and [katex]t[/katex] is the time. |
| 4 | [katex]v_f = v – \frac{F}{m}t[/katex] | Substituting for [katex]a[/katex] in the kinematic equation. Note that different masses will lead to different decelerations if [katex]F[/katex] is constant. |
| 5 | [katex]\Delta s = v_it + \frac{1}{2}at^2[/katex] | The distance [katex]\Delta s[/katex] traveled under acceleration (deceleration in this case) is found using this formula, where the initial speed [katex]v_i[/katex] is [katex]v[/katex], and the acceleration [katex]a[/katex] is known. |
| 6 | [katex]D = vt – \frac{F}{2m}t^2[/katex] | Substituting [katex]-a[/katex] (since it’s deceleration) and simplifying, configuring the equation in terms of [katex]t[/katex]. |
| 7 | Solve for [katex] t [/katex] | Solve the quadratic equation for [katex] t [/katex] to find the time each vehicle takes to travel the distance [katex] D [/katex]. Each vehicle, having different mass, will have a different [katex] t [/katex]. |
| 8 | [katex]\text{Work done, } W = F \times D[/katex] | The work done by the friction force over the distance [katex] D [/katex] is the product of the force and the distance, which is the same for both since both [katex] F [/katex] and [katex] D [/katex] are constant. |
| 9 | [katex]P = \frac{W}{t}[/katex] | Power [katex] P [/katex] is defined as work done per unit time. Given the same work done but different times, power will be different. |
| 10 | [katex]KE = \frac{1}{2}mv^2_f[/katex] | The kinetic energy at any point in time can be calculated using the mass and the velocity at that time. Since both mass and [katex]v_f[/katex] differ for the two vehicles, kinetic energy will also differ. |
Correct answers based on these steps:
– (c) The work done on both vehicles is the same – since they are subject to the same force over the same distance. Other statements are false due to different masses and resulting differences in acceleration, velocity, time, and power.
Just ask: "Help me solve this problem."
An object with a mass m = 80 g is attached to a spring with a force constant k = 25 N/m. The spring is stretched 52.0 cm and released from rest. If it is oscillating on a horizontal frictionless surface, determine the velocity of the mass when it is halfway to the equilibrium position.
A ski lift carries skiers along a 695 meter slope inclined at 34°. To lift a single rider, it is necessary to move 72 kg of mass to the top of the lift. Under maximum load conditions, five riders per minute arrive at the top. If 65 percent of the energy supplied by the motor goes to overcoming friction, what average power must the motor supply?
A ball is thrown straight up. At what point does the ball have the most energy?
The efficiency of a pulley system is 55%. The
pulleys are used to raise a mass of 90.0 kg to a height of
5.60 m. What force is exerted on the rope of the pulley
system if the rope is pulled for 22 m in order to raise
the mass to the required height?
A 0.5 kg cart, on a frictionless 2 m long table, is being pulled by a 0.1 kg mass connected by a string and hanging over a pulley. The system is released from rest. After the hanging mass falls 0.5 m, calculate the speed of the cart on the table. Use ONLY forces and energy.
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Sale and Terms of Use and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
| Kinematics | Forces |
|---|---|
| \(\Delta x = v_i t + \frac{1}{2} at^2\) | \(F = ma\) |
| \(v = v_i + at\) | \(F_g = \frac{G m_1 m_2}{r^2}\) |
| \(v^2 = v_i^2 + 2a \Delta x\) | \(f = \mu N\) |
| \(\Delta x = \frac{v_i + v}{2} t\) | \(F_s =-kx\) |
| \(v^2 = v_f^2 \,-\, 2a \Delta x\) |
| Circular Motion | Energy |
|---|---|
| \(F_c = \frac{mv^2}{r}\) | \(KE = \frac{1}{2} mv^2\) |
| \(a_c = \frac{v^2}{r}\) | \(PE = mgh\) |
| \(T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{r}{g}}\) | \(KE_i + PE_i = KE_f + PE_f\) |
| \(W = Fd \cos\theta\) |
| Momentum | Torque and Rotations |
|---|---|
| \(p = mv\) | \(\tau = r \cdot F \cdot \sin(\theta)\) |
| \(J = \Delta p\) | \(I = \sum mr^2\) |
| \(p_i = p_f\) | \(L = I \cdot \omega\) |
| Simple Harmonic Motion | Fluids |
|---|---|
| \(F = -kx\) | \(P = \frac{F}{A}\) |
| \(T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{l}{g}}\) | \(P_{\text{total}} = P_{\text{atm}} + \rho gh\) |
| \(T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}\) | \(Q = Av\) |
| \(x(t) = A \cos(\omega t + \phi)\) | \(F_b = \rho V g\) |
| \(a = -\omega^2 x\) | \(A_1v_1 = A_2v_2\) |
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| [katex]g[/katex] | Acceleration due to gravity, typically [katex]9.8 , \text{m/s}^2[/katex] on Earth’s surface |
| [katex]G[/katex] | Universal Gravitational Constant, [katex]6.674 \times 10^{-11} , \text{N} \cdot \text{m}^2/\text{kg}^2[/katex] |
| [katex]\mu_k[/katex] and [katex]\mu_s[/katex] | Coefficients of kinetic ([katex]\mu_k[/katex]) and static ([katex]\mu_s[/katex]) friction, dimensionless. Static friction ([katex]\mu_s[/katex]) is usually greater than kinetic friction ([katex]\mu_k[/katex]) as it resists the start of motion. |
| [katex]k[/katex] | Spring constant, in [katex]\text{N/m}[/katex] |
| [katex] M_E = 5.972 \times 10^{24} , \text{kg} [/katex] | Mass of the Earth |
| [katex] M_M = 7.348 \times 10^{22} , \text{kg} [/katex] | Mass of the Moon |
| [katex] M_M = 1.989 \times 10^{30} , \text{kg} [/katex] | Mass of the Sun |
| Variable | SI Unit |
|---|---|
| [katex]s[/katex] (Displacement) | [katex]\text{meters (m)}[/katex] |
| [katex]v[/katex] (Velocity) | [katex]\text{meters per second (m/s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]a[/katex] (Acceleration) | [katex]\text{meters per second squared (m/s}^2\text{)}[/katex] |
| [katex]t[/katex] (Time) | [katex]\text{seconds (s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]m[/katex] (Mass) | [katex]\text{kilograms (kg)}[/katex] |
| Variable | Derived SI Unit |
|---|---|
| [katex]F[/katex] (Force) | [katex]\text{newtons (N)}[/katex] |
| [katex]E[/katex], [katex]PE[/katex], [katex]KE[/katex] (Energy, Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy) | [katex]\text{joules (J)}[/katex] |
| [katex]P[/katex] (Power) | [katex]\text{watts (W)}[/katex] |
| [katex]p[/katex] (Momentum) | [katex]\text{kilogram meters per second (kgm/s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]\omega[/katex] (Angular Velocity) | [katex]\text{radians per second (rad/s)}[/katex] |
| [katex]\tau[/katex] (Torque) | [katex]\text{newton meters (Nm)}[/katex] |
| [katex]I[/katex] (Moment of Inertia) | [katex]\text{kilogram meter squared (kgm}^2\text{)}[/katex] |
| [katex]f[/katex] (Frequency) | [katex]\text{hertz (Hz)}[/katex] |
General Metric Conversion Chart
Example of using unit analysis: Convert 5 kilometers to millimeters.
Start with the given measurement: [katex]\text{5 km}[/katex]
Use the conversion factors for kilometers to meters and meters to millimeters: [katex]\text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}}[/katex]
Perform the multiplication: [katex]\text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}} = 5 \times 10^3 \times 10^3 \, \text{mm}[/katex]
Simplify to get the final answer: [katex]\boxed{5 \times 10^6 \, \text{mm}}[/katex]
Prefix | Symbol | Power of Ten | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
Pico- | p | [katex]10^{-12}[/katex] | 0.000000000001 |
Nano- | n | [katex]10^{-9}[/katex] | 0.000000001 |
Micro- | µ | [katex]10^{-6}[/katex] | 0.000001 |
Milli- | m | [katex]10^{-3}[/katex] | 0.001 |
Centi- | c | [katex]10^{-2}[/katex] | 0.01 |
Deci- | d | [katex]10^{-1}[/katex] | 0.1 |
(Base unit) | – | [katex]10^{0}[/katex] | 1 |
Deca- or Deka- | da | [katex]10^{1}[/katex] | 10 |
Hecto- | h | [katex]10^{2}[/katex] | 100 |
Kilo- | k | [katex]10^{3}[/katex] | 1,000 |
Mega- | M | [katex]10^{6}[/katex] | 1,000,000 |
Giga- | G | [katex]10^{9}[/katex] | 1,000,000,000 |
Tera- | T | [katex]10^{12}[/katex] | 1,000,000,000,000 |
The most advanced version of Phy. 50% off, for early supporters. Prices increase soon.
per month
Billed Monthly. Cancel Anytime.
Trial –> Phy Pro
A quick explanation
Credits are used to grade your FRQs and GQs. Pro users get unlimited credits.
Submitting counts as 1 attempt.
Viewing answers or explanations count as a failed attempts.
Phy gives partial credit if needed
MCQs and GQs are are 1 point each. FRQs will state points for each part.
Phy customizes problem explanations based on what you struggle with. Just hit the explanation button to see.
Understand you mistakes quicker.
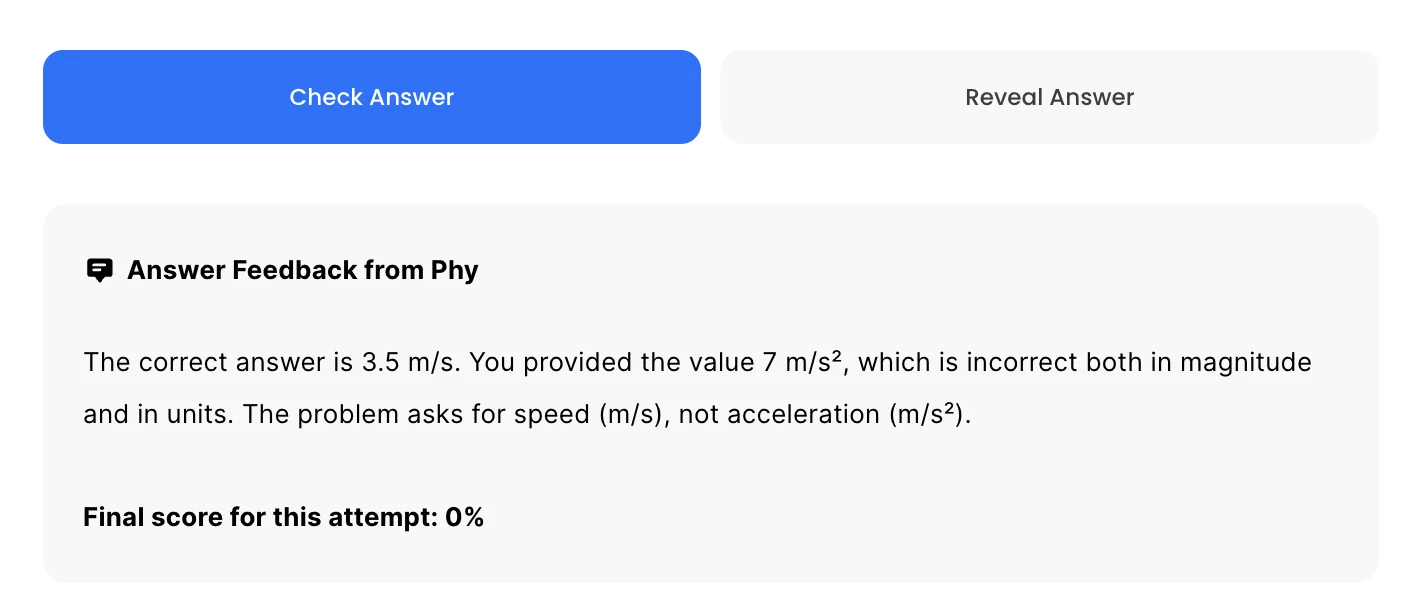
Phy automatically provides feedback so you can improve your responses.
10 Free Credits To Get You Started
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.