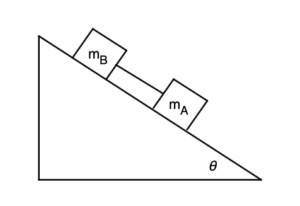
Two blocks made of different materials, connected by a thin cord, slide down a plane ramp inclined at an angle above the horizontal. If the coefficients of friction are and and if , determine:
0 attempts
0% avg
10 UBQ Credits

Two blocks made of different materials, connected by a thin cord, slide down a plane ramp inclined at an angle θ=32∘ above the horizontal. If the coefficients of friction are μA=0.2 and μB=0.3 and if mA=mB=5.0 kg, determine:
| Step | Derivation/Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fgx=mgsinθ | Calculate the component of gravitational force along the incline for one block. |
| 2 | FfA=μAmAgcosθ | Calculate the frictional force for block A. Frictional force is the product of the friction coefficient, mass, gravitational acceleration, and the cosine of the incline angle. |
| 3 | FfB=μBmBgcosθ | Calculate the frictional force for block B using its coefficient of friction. |
| 4 | Fnet=2Fgx–FfA–FfB | Net force is the sum of both gravitational components minus the frictional forces for both blocks. |
| 5 | Fnet=2(mgsinθ)–(μAmgcosθ +μBmgcosθ) |
Substitute the expressions for gravitational and frictional forces into the net force equation. |
| 6 | Fnet= 2⋅5⋅9.8sin(32)–(0.2⋅5⋅9.8cos(32)
+0.3⋅5⋅9.8cos(32)) |
Substitute known values: m=5 kg, g=9.8 m/s2, θ=32∘. |
| 7 | Fnet=52.012–8.3–12.5=
31.2 N |
Calculate the net force acting on both blocks by subtracting the calculated frictional forces from the gravitational force component. |
| 8 | a=2mFnet=2×531.2 | Use Newton’s second law F=ma to solve for acceleration. |
| 9 | 3.1 m/s2 | Calculate the acceleration of the blocks. |
| Step | Derivation/Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | T=mAgsinθ–FfA–mAa | Consider block A. The tension is the net force after subtracting the force needed for acceleration and friction. |
| 2 | T=5⋅9.8sin(32)–(0.2⋅5⋅9.8cos(32))–5⋅3.1 | Substitute known values for mass, gravitational acceleration, incline angle, friction coefficient, and acceleration. |
| 3 | T=26–8.3–15.6=2.1 N | Calculate the tension in the cord between the blocks. |
| 4 | 2.1 N | Express the tension in the cord as the final answer. |
Just ask: "Help me solve this problem."
Two objects (49.0 and 24.0 kg) are connected by a massless string that passes over a massless, frictionless pulley. The pulley hangs from the ceiling. Find the acceleration of the objects and the tension in the string.
There are two cables that lift an elevator, each with a force of 10,000 N. The 1,000 kg elevator is lifted from the first floor and accelerates over 10 m until it reaches its top speed of 6 m/s. What is the mass of the people in the elevator?
A ball falls straight down through the air under the influence of gravity. There is a retarding force F on the ball with magnitude given by F=bv, where v is the speed of the ball and b is a positive constant. The ball reaches a terminal velocity after a time t. The magnitude of the acceleration at time t/2 is
Why do raindrops fall with constant speed during the later stages of their descent?
A student is watching their hockey puck slide up and down an incline. They give the puck a quick push along a frictionless table, and it slides up a 30° rough incline (µk = .4) of distance d, with an initial speed of 5 m/s, and then it slides back down.
Two objects (49.0 and 24.0 kg) are connected by a massless string that passes over a massless, frictionless pulley. The pulley hangs from the ceiling. Find the acceleration of the objects and the tension in the string.
There are two cables that lift an elevator, each with a force of 10,000 N. The 1,000 kg elevator is lifted from the first floor and accelerates over 10 m until it reaches its top speed of 6 m/s. What is the mass of the people in the elevator?
A quick explanation
Credits are used to grade your FRQs and GQs. Pro users get unlimited credits.
Submitting counts as 1 attempt.
Viewing answers or explanations count as a failed attempts.
Phy gives partial credit if needed
MCQs and GQs are are 1 point each. FRQs will state points for each part.
Phy customizes problem explanations based on what you struggle with. Just hit the explanation button to see.
Understand you mistakes quicker.
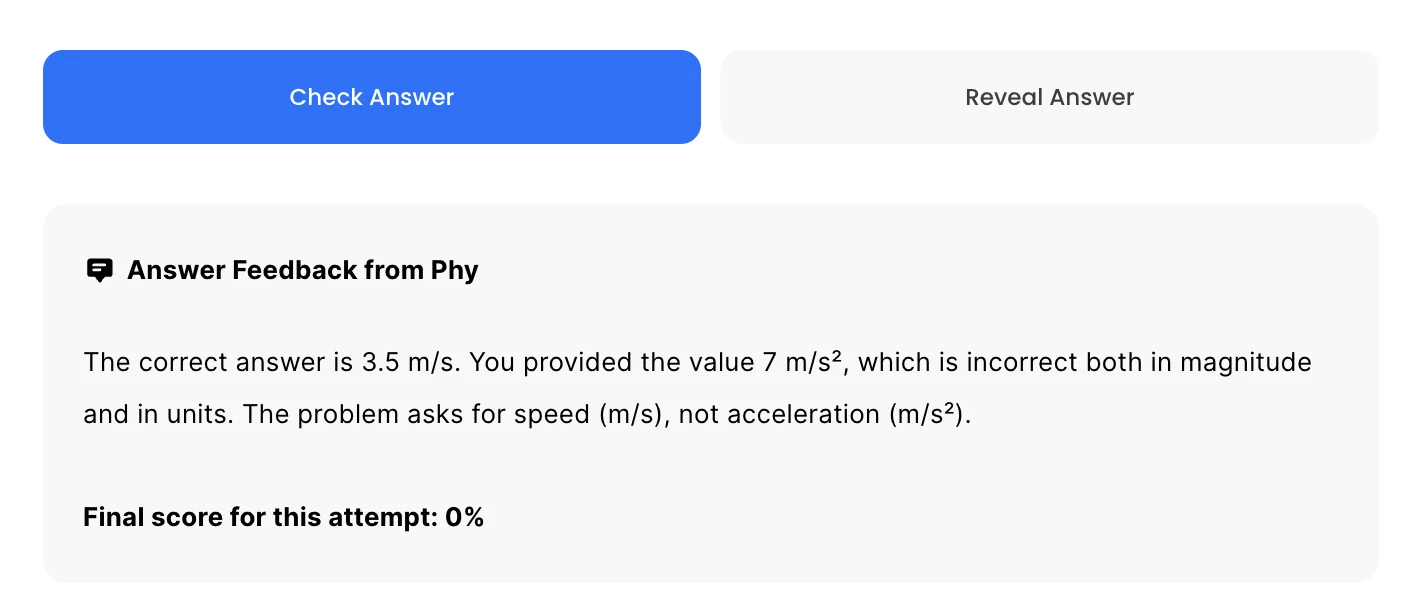
Phy automatically provides feedback so you can improve your responses.
10 Free Credits To Get You Started
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.