1. Maximum Height Reached by the Stone
| Step | Formula Derivation | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | v^2 = u^2 + 2as | Kinematic equation, with v as final velocity (0 at max height), u as initial velocity, a as acceleration (gravity), and s as displacement. |
| 2 | 0 = (8.0, \text{m/s})^2 – 2 \times 9.81, \text{m/s}^2 \times s_{\text{max}} | At max height, final velocity is 0. |
| 3 | Solve for s_{\text{max}} | Maximum height above the cliff. |
2. Time to Reach Maximum Height
| Step | Formula Derivation | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | v = u + at | Kinematic equation for velocity. |
| 2 | 0 = 8.0, \text{m/s} – 9.81, \text{m/s}^2 \times t_{\text{max}} | Final velocity is 0 at max height. |
| 3 | Solve for t_{\text{max}} | Time to reach max height. |
3. Height of the Cliff
Total Time from Throw to Sea
| Step | Formula Derivation | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | s = ut + \frac{1}{2}at^2 | Displacement formula for the entire journey, where s is total displacement (height of the cliff), u is initial velocity, t is total time, and a is acceleration (gravity). Note gravity is negative in this case. |
| 2 | s_{\text{cliff}} = 8.0, \text{m/s} \times 3.0, \text{s} – \frac{1}{2} \times 9.81, \text{m/s}^2 \times (3.0, \text{s})^2 | Substituting the values for u, t, and g. |
| 3 | Solve for s_{\text{cliff}} | Height of the cliff. |
Performing the calculations above yield the following results:
Phy can also check your working. Just snap a picture!
Two students are on a balcony 19.6 m above the street. One student throws a ball vertically downward at 14.7 m/s. At the same instant, the other student throws a ball vertically upward at the same speed. The second ball just misses the balcony on the way down.
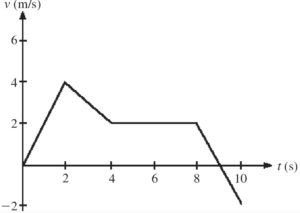
The figure shows the velocity-versus-time graph for a basketball player traveling up and down the court in a straight-line path. Find the displacement of the player…
A rocket, initially at rest, is fired vertically upward with an acceleration of 12.0 m/s2. At an altitude of 1.00 km, the rocket engine cuts off. Drag is negligible.
A car decelerates from 25 \, m/s to 5 \, m/s at 10 \, m/s^2. How far does the car travel during this deceleration?
A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly over a time of 5 seconds for a distance of 100 m. Determine the acceleration of the car.
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Sale and Terms of Use and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
| Kinematics | Forces |
|---|---|
| \Delta x = v_i t + \frac{1}{2} at^2 | F = ma |
| v = v_i + at | F_g = \frac{G m_1m_2}{r^2} |
| a = \frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t} | f = \mu N |
| R = \frac{v_i^2 \sin(2\theta)}{g} |
| Circular Motion | Energy |
|---|---|
| F_c = \frac{mv^2}{r} | KE = \frac{1}{2} mv^2 |
| a_c = \frac{v^2}{r} | PE = mgh |
| KE_i + PE_i = KE_f + PE_f |
| Momentum | Torque and Rotations |
|---|---|
| p = m v | \tau = r \cdot F \cdot \sin(\theta) |
| J = \Delta p | I = \sum mr^2 |
| p_i = p_f | L = I \cdot \omega |
| Simple Harmonic Motion |
|---|
| F = -k x |
| T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{l}{g}} |
| T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k}} |
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| g | Acceleration due to gravity, typically 9.8 , \text{m/s}^2 on Earth’s surface |
| G | Universal Gravitational Constant, 6.674 \times 10^{-11} , \text{N} \cdot \text{m}^2/\text{kg}^2 |
| \mu_k and \mu_s | Coefficients of kinetic (\mu_k) and static (\mu_s) friction, dimensionless. Static friction (\mu_s) is usually greater than kinetic friction (\mu_k) as it resists the start of motion. |
| k | Spring constant, in \text{N/m} |
| M_E = 5.972 \times 10^{24} , \text{kg} | Mass of the Earth |
| M_M = 7.348 \times 10^{22} , \text{kg} | Mass of the Moon |
| M_M = 1.989 \times 10^{30} , \text{kg} | Mass of the Sun |
| Variable | SI Unit |
|---|---|
| s (Displacement) | \text{meters (m)} |
| v (Velocity) | \text{meters per second (m/s)} |
| a (Acceleration) | \text{meters per second squared (m/s}^2\text{)} |
| t (Time) | \text{seconds (s)} |
| m (Mass) | \text{kilograms (kg)} |
| Variable | Derived SI Unit |
|---|---|
| F (Force) | \text{newtons (N)} |
| E, PE, KE (Energy, Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy) | \text{joules (J)} |
| P (Power) | \text{watts (W)} |
| p (Momentum) | \text{kilogram meters per second (kgm/s)} |
| \omega (Angular Velocity) | \text{radians per second (rad/s)} |
| \tau (Torque) | \text{newton meters (Nm)} |
| I (Moment of Inertia) | \text{kilogram meter squared (kgm}^2\text{)} |
| f (Frequency) | \text{hertz (Hz)} |
General Metric Conversion Chart
Example of using unit analysis: Convert 5 kilometers to millimeters.
Start with the given measurement: \text{5 km}
Use the conversion factors for kilometers to meters and meters to millimeters: \text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}}
Perform the multiplication: \text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}} = 5 \times 10^3 \times 10^3 \, \text{mm}
Simplify to get the final answer: \boxed{5 \times 10^6 \, \text{mm}}
Prefix | Symbol | Power of Ten | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
Pico- | p | 10^{-12} | 0.000000000001 |
Nano- | n | 10^{-9} | 0.000000001 |
Micro- | µ | 10^{-6} | 0.000001 |
Milli- | m | 10^{-3} | 0.001 |
Centi- | c | 10^{-2} | 0.01 |
Deci- | d | 10^{-1} | 0.1 |
(Base unit) | – | 10^{0} | 1 |
Deca- or Deka- | da | 10^{1} | 10 |
Hecto- | h | 10^{2} | 100 |
Kilo- | k | 10^{3} | 1,000 |
Mega- | M | 10^{6} | 1,000,000 |
Giga- | G | 10^{9} | 1,000,000,000 |
Tera- | T | 10^{12} | 1,000,000,000,000 |
The most advanced version of Phy. Currently 50% off, for early supporters.
per month
Billed Monthly. Cancel Anytime.
Trial –> Phy Pro
A quick explanation
UBQ credits are specifically used to grade your FRQs and GQs.
You can still view questions and see answers without credits.
Submitting an answer counts as 1 attempt.
Seeing answer or explanation counts as a failed attempt.
Lastly, check your average score, across every attempt, in the top left.
MCQs are 1 point each. GQs are 1 point. FRQs will state points for each part.
Phy can give partial credit for GQs & FRQs.
Phy sees everything.
It customizes responses, explanations, and feedback based on what you struggle with. Try your best on every question!
Understand you mistakes quicker.
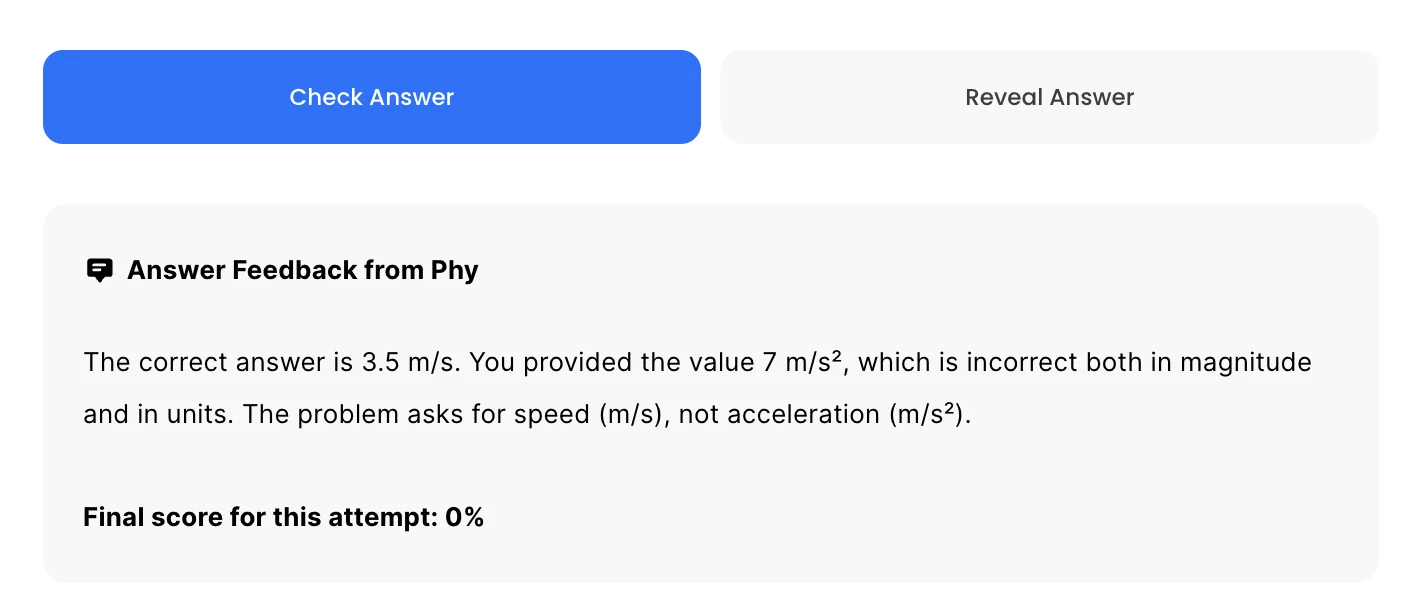
For GQs and FRQs, Phy provides brief feedback as to how you can improve your answer.
Aim to increase your understadning and average score with every attempt!
10 Free Credits To Get You Started
*Phy Pro members get unlimited credits
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.