Which pair of quantities will always have the same magnitude if motion is in a straight line and in one direction?
A \(350\ \text{g}\) ball is attached to the end of a thin, uniform rod of mass \(500\ \text{g}\) and length \(1.2\ \text{m}\). The system is rotated in a horizontal circle about the opposite end of the rod. Calculate the moment of inertia of the system about the axis of rotation. Hint: the moment of inertia of a thin rod about the end of the rod is \(I = \tfrac{1}{3} m L^2\).
A car moving at 30 m/s makes a head-on collision with a stone wall. From what height would the car have to fall in order to make an equally hard collision with the ground?
A ball is thrown straight up. At what point does the ball have the most energy?
Why do you need to “pump” your legs when you begin swinging on a park swing?
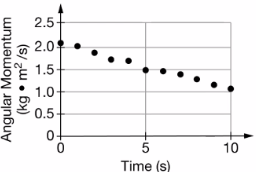
During the experiment, students collect data about the angular momentum of a rigid, uniform spinning wheel about an axle as a function of time, which was used to create the graph that is shown. A frictional torque is exerted on the wheel. A student makes the following statement about the data. “The frictional torque exerted on the wheel is independent of the wheel’s angular speed.” Does the data from the graph support the student’s statement? Justify your selection.
A gun can fire a bullet to height \( h \) when fired straight up. If the same gun is pointed at an angle of \( 45^\circ \) from the vertical, what is the new maximum height of the projectile?
A pendulum consists of a ball of mass \( m \) suspended at the end of a massless cord of length \( L \). The pendulum is drawn aside through an angle of \( 60^\circ \) with the vertical and released. At the low point of its swing, the speed of the pendulum ball is
When we refer to an object’s speed, we’re talking about:
Suppose just two external forces act on a stationary, rigid object and the two forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Under what condition does the object start to rotate?
A car rounds a curve at a steady \( 50 \) \( \text{km/h} \). If it rounds the same curve at a steady \( 70 \) \( \text{km/h} \), will its acceleration be any different?
A circus cannon fires an acrobat into the air at an angle of \( 45^\circ \) above the horizontal, and the acrobat reaches a maximum height \( y \) above her original launch height. The cannon is now aimed so that it fires straight up, at an identical speed, into the air at an angle of \( 90^\circ \) to the horizontal. In terms of \( y \), what is the acrobat’s new maximum height?
A skateboarder, with an initial speed of \( 20.0 \, \text{m/s} \), rolls to the end of friction-free incline of length \( 25 \, \text{m} \). At what angle is the incline oriented above the horizontal?
An arrow is shot horizontally from a distance of \( 20 \, \text{m} \) away. It lands \( 0.05 \, \text{m} \) below the center of the target. If air resistance is negligible, what was the initial speed of the arrow?
A driver is traveling at a speed of \( 18.0 \) \( \text{m/s} \) when she sees a red light ahead. Her car is capable of decelerating at a rate of \( 3.65 \) \( \text{m/s}^2 \). If it takes her \( 0.350 \) \( \text{s} \) to get the brakes on and she is \( 20.0 \) \( \text{m} \) from the intersection when she sees the light, will she be able to stop in time? How far from the beginning of the intersection will she be, and in what direction?
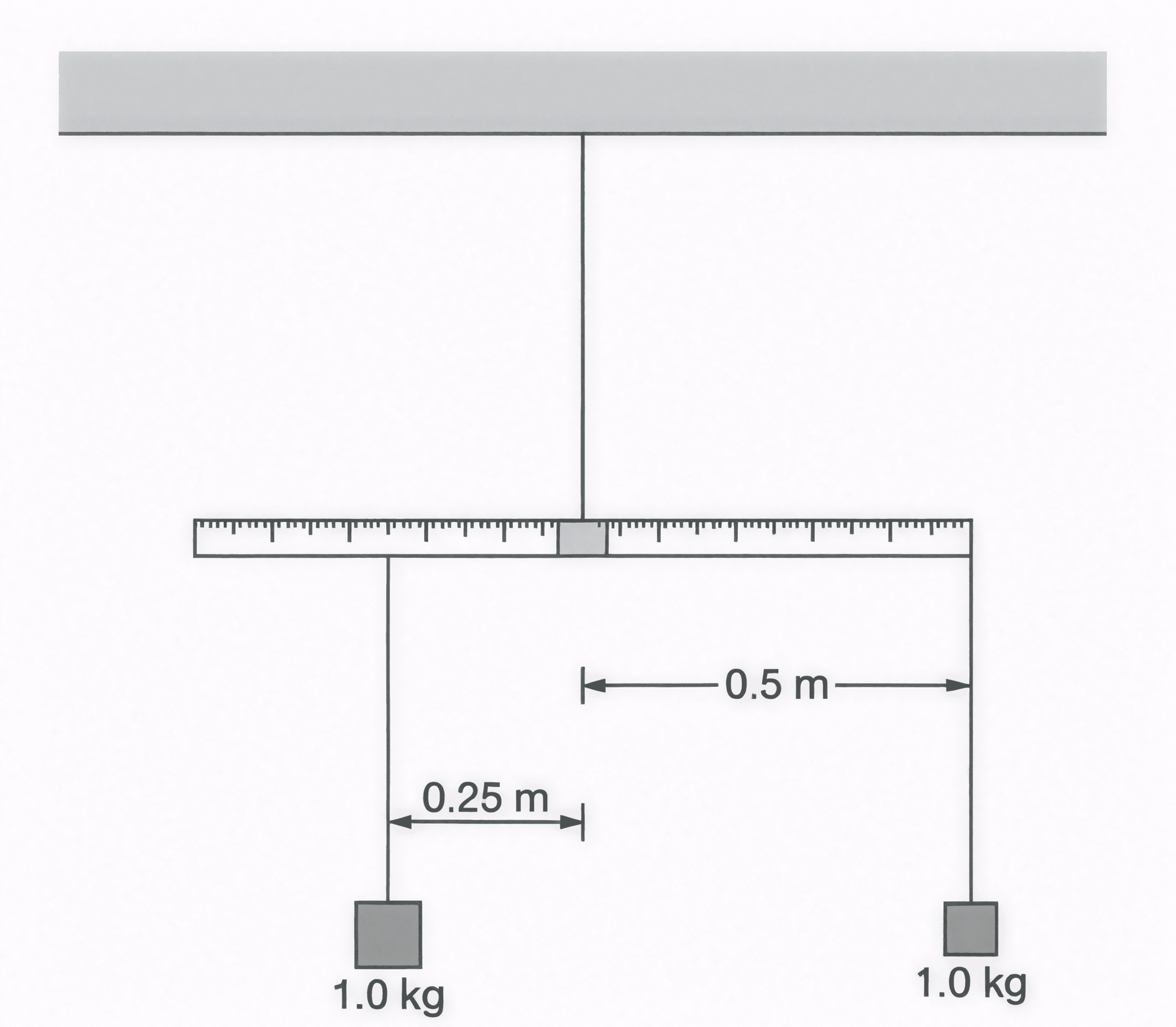
A meterstick is supported at its center, which is aligned with the center of a cradle located at position \( x = 0 \) \( \text{m} \). Two identical objects of mass \( 1.0 \) \( \text{kg} \) are suspended from the meterstick. One object hangs \( 0.25 \) \( \text{m} \) to the left of the support point, and the other object hangs \( 0.50 \) \( \text{m} \) to the right of the support point. The system is released from rest and is free to rotate. Which of the following claims correctly describes the subsequent motion of the system containing the meterstick, cradle, and the two objects?
Which of the following do not affect the maximum speed that a car can drive in a circle? Choose both correct answers.
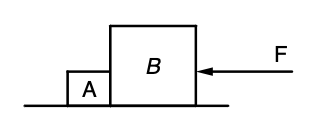
In the diagram shown, a \(20 \, \text{N}\) force is applied to block \(B\) (\(7 \, \text{kg}\)). Block \(A\) has a mass of \(3 \, \text{kg}\). Assume frictionless conditions.
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.