for free to use all UBQ features
A block is projected up a ramp with an initial speed \( v_0 \). It travels along the surface of the ramp with constant acceleration \( a \). Take the positive direction of motion to be up the ramp. If the acceleration vector points opposite the initial velocity vector, which of the following MUST be true?
Are astronauts really “weightless” while in orbit?
Why are doorknobs located on the side of the door opposite the hinges?
A rescue plane wants to drop supplies to isolated mountain climbers on a rocky ridge that is \( 235 \) \( \text{m} \) below. The plane is traveling horizontally with a speed of \( 250 \) \( \text{km/h} \). How far in advance of the recipients (horizontal distance) must the goods be dropped?
A spacecraft somewhere in between the Earth and the Moon experiences zero net force acting on it. This is because the Earth and the Moon pull the spacecraft in equal but opposite directions. Find the distance \(D\) away from Earth such that the spacecraft experiences zero net force. The distance between the Moon and Earth is \(\sim 3.844 \times 10^8 \, \text{m}\).
Note: You may need the mass of the Earth and the Moon. You can find this in the formula table.

Which statement is true about the distances the two objects have traveled at time \( t_f \)?
A car is traveling 20 m/s when the driver sees a child standing on the road. She takes 0.8 s to react then steps on the brakes and slows at 7.0 m/s2. How far does the car go before it stops?
A car is moving up the side of a circular roller coaster loop of radius \( 12 \) \( \text{m} \). The angular velocity is \( 1.8 \) \( \text{rad/s} \) and angular acceleration is \( -0.82 \) \( \text{rad/s}^2 \). The car is at the same elevation as the center of the loop. Find the magnitude and direction (relative to the horizontal) of the acceleration.
A \( 60 \ \text{kg} \) person is riding in an elevator. At time \( t_1 \), the elevator is accelerating downward with a magnitude of \( 2 \ \text{m/s}^2 \). A short time later, at time \( t_2 \), the elevator is accelerating upward with a magnitude of \( 2 \ \text{m/s}^2 \). The ratio of the normal force exerted by the elevator on the person at time \( t_1 \) to that at time \( t_2 \) is most nearly
An object weighs \( 300 \, \text{N} \) on Earth and \( 50 \, \text{N} \) on the Moon. Does the object have less inertia on the Moon?
Two equal-magnitude forces are applied to a door at the doorknob. The first force is applied perpendicular to the door, and the second force is applied at \( 30^\circ \) to the plane of the door. Which force exerts the greater torque about the door hinge?
A rocket launches upward by expelling exhaust gases downward. This is an illustration of Newton’s ____ Law.
A \(5\)-meter long ladder is leaning against a wall, with the bottom of the ladder \(3\) meters from the wall. The ladder is uniform and has a mass of \(20 \, \text{kg}\). A person of mass \(80 \, \text{kg}\) is standing on the ladder at a distance of \(4\) meters from the bottom of the ladder. What is the force exerted by the wall on the ladder?
A \(2,000 \, \text{kg}\) car collides with a stationary \(1,000 \, \text{kg}\) car. Afterwards, they slide \(6 \, \text{m}\) before coming to a stop. The coefficient of friction between the tires and the road is \(0.7\). Find the initial velocity of the \(2,000 \, \text{kg}\) car before the collision?
A \( 0.72 \) \( \text{m} \)-diameter solid sphere can be rotated about an axis through its center by a torque of \( 10.8 \) \( \text{Nm} \) which accelerates it uniformly from rest through a total of \( 160 \) revolutions in \( 15.0 \) \( \text{s} \). What is the mass of the sphere?
A bullet moving with an initial speed of \( v_o \) strikes and embeds itself in a block of wood which is suspended by a string, causing the bullet and block to rise to a maximum height \( h \). Which of the following statements is true of the collision.
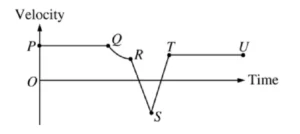 The graph above shows velocity as a function of time for an object moving along a straight line. For which of the following sections of the graph is the acceleration constant and nonzero?
The graph above shows velocity as a function of time for an object moving along a straight line. For which of the following sections of the graph is the acceleration constant and nonzero?
A officer fires a pistol horizontally toward a target \(120 \,\text{m}\) at a velocity of \(200 \, \text{m/s}\). If the officer aimed directly at the bull’s eye
A ball is kicked at a speed of \( v_0 \) at an angle \( \theta \) above the horizontal. The ball travels 25 meters horizontally. If the ball is kicked at \( 2v_0 \), what will the horizontal displacement be?
A curve with a radius of \( 125 \) \( \text{m} \) is properly banked for a car traveling \( 40 \) \( \text{m/s} \). What must be the coefficient of static friction \( (\mu_s) \) for a car not to skid on the same curve when traveling at \( 53 \) \( \text{m/s} \)?
Why do you tend to slide across the car seat when the car makes a sharp turn?
Two satellites of equal mass, \( S_1 \) and \( S_2 \), orbit the Earth. \( S_1 \) is orbiting at a distance \( r \) from the Earth’s center at speed \( v \). \( S_2 \) orbits at a distance \( 2r \) from the Earth’s centre at speed \( \dfrac{v}{\sqrt{2}} \). The ratio of the centripetal force on \( S_1 \) to the centripetal force on \( S_2 \) is
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.