| Step | Derivation/Formula | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | t_1 = \sqrt{\frac{2 h_1}{g}} | Calculate the time to reach the maximum height of the first bounce. This formula comes from the kinematic equation h = \frac{1}{2} g t^2 . |
| 2 | t_{\text{total}} = 2 t_1 | Time in the air includes both going up and coming down, hence the total time is twice the time to reach maximum height. |
| 3 | 1 = 2 \sqrt{\frac{2 h_1}{g}} | Given that the total time between the first and second bounce is 1 second, use this to find h_1 . |
| 4 | \sqrt{\frac{2 h_1}{g}} = 0.5 | Isolate the term with height h_1 on one side. |
| 5 | \frac{2 h_1}{g} = 0.25 | Square both sides to eliminate the square root. |
| 6 | h_1 = 0.125 g | Solve for h_1 in terms of g . This gives the height of the first bounce. |
| 7 | h_2 = \frac{h_1}{2} = 0.0625 g | Calculate the height of the second bounce, which is half of the first bounce. |
| 8 | t_2 = \sqrt{\frac{2 h_2}{g}} = \sqrt{\frac{2 \cdot 0.0625 g}{g}} | Calculate the time to reach the maximum height of the second bounce. |
| 9 | t_2 = \sqrt{0.125} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{8}} \approx 0.354 \text{ seconds} | Simplify to find the time to reach maximum height of the second bounce. |
| 10 | t_{\text{total, 2nd bounce}} = 2 \times 0.354 = 0.707 \text{ seconds} | The total time in the air for the second bounce is twice the time to reach maximum height. |
| 11 | \boxed{0.71 \text{ seconds}} | The answer is closest to 0.71 seconds, option (b). |
Phy can also check your working. Just snap a picture!
Two students are on a balcony 19.6 m above the street. One student throws a ball vertically downward at 14.7 m/s. At the same instant, the other student throws a ball vertically upward at the same speed. The second ball just misses the balcony on the way down.
An object is projected vertically upward from ground level. It rises to a maximum height H . If air resistance is negligible, which of the following must be true for the object when it is at a height H/2 ?
A 10kg box is pushed to the right by an unknown force at an angle of 25° below the horizontal while a friction force of 50 N acts on the box as well. The box accelerates from rest and travels a distance of 4 m where it is moving at 3 m/s. Solve the following without the use of energy.
An object of unknown mass is acted upon by multiple forces:
The coefficients of friction are μs=0.6 and μk=0.2. Starting from rest, the object travels 10 meters in 4.5 seconds. What is the mass of the unknown object?
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Sale and Terms of Use and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
| Kinematics | Forces |
|---|---|
| \Delta x = v_i t + \frac{1}{2} at^2 | F = ma |
| v = v_i + at | F_g = \frac{G m_1m_2}{r^2} |
| a = \frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t} | f = \mu N |
| R = \frac{v_i^2 \sin(2\theta)}{g} |
| Circular Motion | Energy |
|---|---|
| F_c = \frac{mv^2}{r} | KE = \frac{1}{2} mv^2 |
| a_c = \frac{v^2}{r} | PE = mgh |
| KE_i + PE_i = KE_f + PE_f |
| Momentum | Torque and Rotations |
|---|---|
| p = m v | \tau = r \cdot F \cdot \sin(\theta) |
| J = \Delta p | I = \sum mr^2 |
| p_i = p_f | L = I \cdot \omega |
| Simple Harmonic Motion |
|---|
| F = -k x |
| T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{l}{g}} |
| T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k}} |
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| g | Acceleration due to gravity, typically 9.8 , \text{m/s}^2 on Earth’s surface |
| G | Universal Gravitational Constant, 6.674 \times 10^{-11} , \text{N} \cdot \text{m}^2/\text{kg}^2 |
| \mu_k and \mu_s | Coefficients of kinetic (\mu_k) and static (\mu_s) friction, dimensionless. Static friction (\mu_s) is usually greater than kinetic friction (\mu_k) as it resists the start of motion. |
| k | Spring constant, in \text{N/m} |
| M_E = 5.972 \times 10^{24} , \text{kg} | Mass of the Earth |
| M_M = 7.348 \times 10^{22} , \text{kg} | Mass of the Moon |
| M_M = 1.989 \times 10^{30} , \text{kg} | Mass of the Sun |
| Variable | SI Unit |
|---|---|
| s (Displacement) | \text{meters (m)} |
| v (Velocity) | \text{meters per second (m/s)} |
| a (Acceleration) | \text{meters per second squared (m/s}^2\text{)} |
| t (Time) | \text{seconds (s)} |
| m (Mass) | \text{kilograms (kg)} |
| Variable | Derived SI Unit |
|---|---|
| F (Force) | \text{newtons (N)} |
| E, PE, KE (Energy, Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy) | \text{joules (J)} |
| P (Power) | \text{watts (W)} |
| p (Momentum) | \text{kilogram meters per second (kgm/s)} |
| \omega (Angular Velocity) | \text{radians per second (rad/s)} |
| \tau (Torque) | \text{newton meters (Nm)} |
| I (Moment of Inertia) | \text{kilogram meter squared (kgm}^2\text{)} |
| f (Frequency) | \text{hertz (Hz)} |
General Metric Conversion Chart
Example of using unit analysis: Convert 5 kilometers to millimeters.
Start with the given measurement: \text{5 km}
Use the conversion factors for kilometers to meters and meters to millimeters: \text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}}
Perform the multiplication: \text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}} = 5 \times 10^3 \times 10^3 \, \text{mm}
Simplify to get the final answer: \boxed{5 \times 10^6 \, \text{mm}}
Prefix | Symbol | Power of Ten | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
Pico- | p | 10^{-12} | 0.000000000001 |
Nano- | n | 10^{-9} | 0.000000001 |
Micro- | µ | 10^{-6} | 0.000001 |
Milli- | m | 10^{-3} | 0.001 |
Centi- | c | 10^{-2} | 0.01 |
Deci- | d | 10^{-1} | 0.1 |
(Base unit) | – | 10^{0} | 1 |
Deca- or Deka- | da | 10^{1} | 10 |
Hecto- | h | 10^{2} | 100 |
Kilo- | k | 10^{3} | 1,000 |
Mega- | M | 10^{6} | 1,000,000 |
Giga- | G | 10^{9} | 1,000,000,000 |
Tera- | T | 10^{12} | 1,000,000,000,000 |
The most advanced version of Phy. Currently 50% off, for early supporters.
per month
Billed Monthly. Cancel Anytime.
Trial –> Phy Pro
A quick explanation
UBQ credits are specifically used to grade your FRQs and GQs.
You can still view questions and see answers without credits.
Submitting an answer counts as 1 attempt.
Seeing answer or explanation counts as a failed attempt.
Lastly, check your average score, across every attempt, in the top left.
MCQs are 1 point each. GQs are 1 point. FRQs will state points for each part.
Phy can give partial credit for GQs & FRQs.
Phy sees everything.
It customizes responses, explanations, and feedback based on what you struggle with. Try your best on every question!
Understand you mistakes quicker.
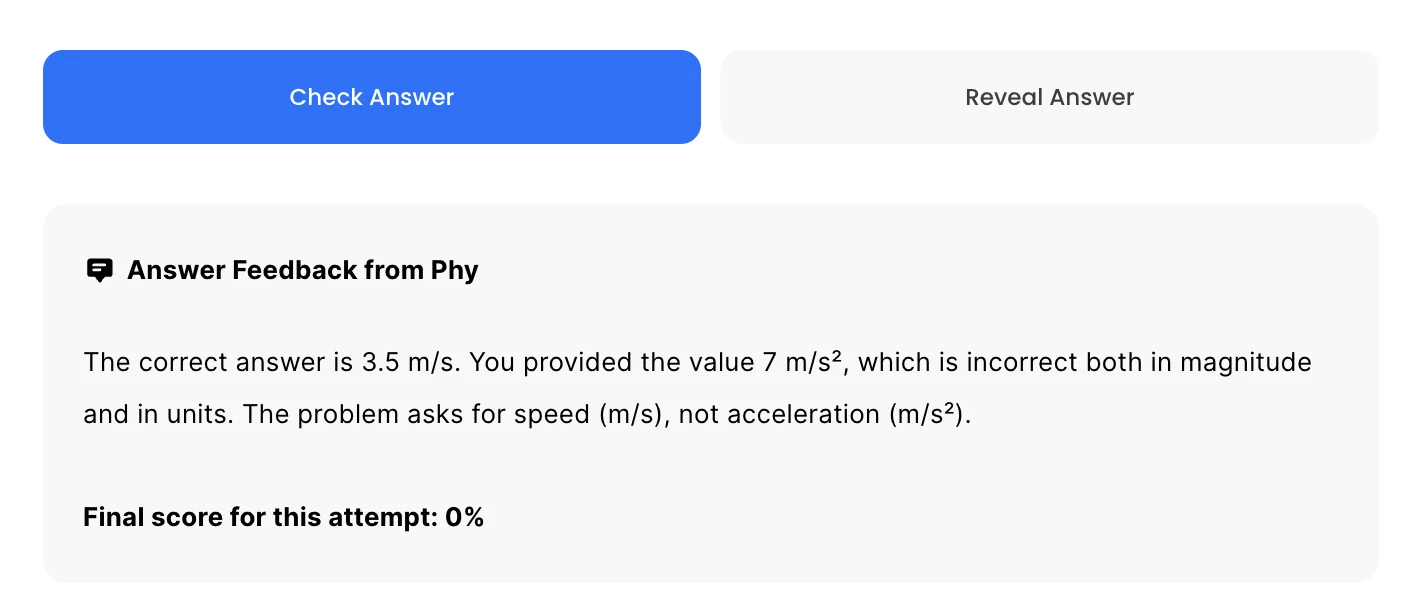
For GQs and FRQs, Phy provides brief feedback as to how you can improve your answer.
Aim to increase your understadning and average score with every attempt!
10 Free Credits To Get You Started
*Phy Pro members get unlimited credits
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.