1. Maximum Height Reached by the Coin
| Step | Formula Derivation | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | v^2 = u^2 + 2as | Kinematic equation for motion, with v as final velocity, u as initial velocity, a as acceleration, and s as displacement. |
| 2 | 0 = (11, \text{m/s})^2 – 2 \times 9.81, \text{m/s}^2 \times s | At maximum height, final velocity v = 0, initial velocity u = 11, \text{m/s} upward, acceleration a = -9.81, \text{m/s}^2 (gravity acts downward). |
| 3 | Solve for s | Calculate the displacement s. |
2. Position 4.20 Seconds After Being Released
| Step | Formula Derivation | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | s = ut + \frac{1}{2}at^2 | Kinematic equation for displacement. |
| 2 | s = 11, \text{m/s} \times 4.20, \text{s} – \frac{1}{2} \times 9.81, \text{m/s}^2 \times (4.20, \text{s})^2 | Substitute values for u, a, and t (time after release). |
3. Velocity 4.20 Seconds After Being Released
| Step | Formula Derivation | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | v = u + at | Kinematic equation for velocity. |
| 2 | v = 11, \text{m/s} – 9.81, \text{m/s}^2 \times 4.20, \text{s} | Substitute values for u, a, and t. |
4. Time Before Coin Hits the Ground
| Step | Formula Derivation | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | s = ut + \frac{1}{2}at^2 | Kinematic equation for displacement. |
| 2 | -250, \text{m} = 11, \text{m/s} \times t – \frac{1}{2} \times 9.81, \text{m/s}^2 \times t^2 | Substitute values for s (downward displacement), u, and a. Solve for t. |
Let’s perform the calculations for each part.
The results for each part are as follows:
Phy can also check your working. Just snap a picture!
A rubber ball bounces on the ground. After each bounce, the ball reaches one-half the height of the bounce before it. If the time the ball was in the air between the first and second bounce was 1 second. What would be the time between the second and third bounce?
A mine shaft is known to be 57.8 m deep. If you dropped a rock down the shaft, how long would it take for you to hear the sound of the rock hitting the bottom of the shaft knowing that sound travels at a constant velocity of 345 m/s?
A ranger in a national park is driving at 56 km/h when a deer jumps onto the road 65 m ahead of the vehicle. After a reaction time of t s, the ranger applies the brakes to produce an acceleration of -3 m/s2. What is the maximum reaction time allowed if the ranger is to avoid hitting the deer?
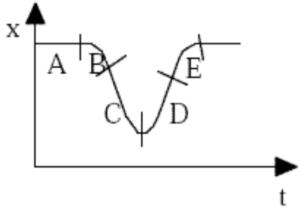 The graph below is a plot of position versus time. For which labeled region is the velocity positive and the acceleration negative?
The graph below is a plot of position versus time. For which labeled region is the velocity positive and the acceleration negative?
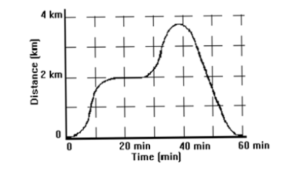
Above is a graph of the distance vs. time for car moving along a road. According the graph, at which of the following times would the automobile have been accelerating positively?
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Sale and Terms of Use and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
| Kinematics | Forces |
|---|---|
| \Delta x = v_i t + \frac{1}{2} at^2 | F = ma |
| v = v_i + at | F_g = \frac{G m_1m_2}{r^2} |
| a = \frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t} | f = \mu N |
| R = \frac{v_i^2 \sin(2\theta)}{g} |
| Circular Motion | Energy |
|---|---|
| F_c = \frac{mv^2}{r} | KE = \frac{1}{2} mv^2 |
| a_c = \frac{v^2}{r} | PE = mgh |
| KE_i + PE_i = KE_f + PE_f |
| Momentum | Torque and Rotations |
|---|---|
| p = m v | \tau = r \cdot F \cdot \sin(\theta) |
| J = \Delta p | I = \sum mr^2 |
| p_i = p_f | L = I \cdot \omega |
| Simple Harmonic Motion |
|---|
| F = -k x |
| T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{l}{g}} |
| T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k}} |
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| g | Acceleration due to gravity, typically 9.8 , \text{m/s}^2 on Earth’s surface |
| G | Universal Gravitational Constant, 6.674 \times 10^{-11} , \text{N} \cdot \text{m}^2/\text{kg}^2 |
| \mu_k and \mu_s | Coefficients of kinetic (\mu_k) and static (\mu_s) friction, dimensionless. Static friction (\mu_s) is usually greater than kinetic friction (\mu_k) as it resists the start of motion. |
| k | Spring constant, in \text{N/m} |
| M_E = 5.972 \times 10^{24} , \text{kg} | Mass of the Earth |
| M_M = 7.348 \times 10^{22} , \text{kg} | Mass of the Moon |
| M_M = 1.989 \times 10^{30} , \text{kg} | Mass of the Sun |
| Variable | SI Unit |
|---|---|
| s (Displacement) | \text{meters (m)} |
| v (Velocity) | \text{meters per second (m/s)} |
| a (Acceleration) | \text{meters per second squared (m/s}^2\text{)} |
| t (Time) | \text{seconds (s)} |
| m (Mass) | \text{kilograms (kg)} |
| Variable | Derived SI Unit |
|---|---|
| F (Force) | \text{newtons (N)} |
| E, PE, KE (Energy, Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy) | \text{joules (J)} |
| P (Power) | \text{watts (W)} |
| p (Momentum) | \text{kilogram meters per second (kgm/s)} |
| \omega (Angular Velocity) | \text{radians per second (rad/s)} |
| \tau (Torque) | \text{newton meters (Nm)} |
| I (Moment of Inertia) | \text{kilogram meter squared (kgm}^2\text{)} |
| f (Frequency) | \text{hertz (Hz)} |
General Metric Conversion Chart
Example of using unit analysis: Convert 5 kilometers to millimeters.
Start with the given measurement: \text{5 km}
Use the conversion factors for kilometers to meters and meters to millimeters: \text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}}
Perform the multiplication: \text{5 km} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{m}}{1 \, \text{km}} \times \frac{10^3 \, \text{mm}}{1 \, \text{m}} = 5 \times 10^3 \times 10^3 \, \text{mm}
Simplify to get the final answer: \boxed{5 \times 10^6 \, \text{mm}}
Prefix | Symbol | Power of Ten | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
Pico- | p | 10^{-12} | 0.000000000001 |
Nano- | n | 10^{-9} | 0.000000001 |
Micro- | µ | 10^{-6} | 0.000001 |
Milli- | m | 10^{-3} | 0.001 |
Centi- | c | 10^{-2} | 0.01 |
Deci- | d | 10^{-1} | 0.1 |
(Base unit) | – | 10^{0} | 1 |
Deca- or Deka- | da | 10^{1} | 10 |
Hecto- | h | 10^{2} | 100 |
Kilo- | k | 10^{3} | 1,000 |
Mega- | M | 10^{6} | 1,000,000 |
Giga- | G | 10^{9} | 1,000,000,000 |
Tera- | T | 10^{12} | 1,000,000,000,000 |
The most advanced version of Phy. Currently 50% off, for early supporters.
per month
Billed Monthly. Cancel Anytime.
Trial –> Phy Pro
A quick explanation
UBQ credits are specifically used to grade your FRQs and GQs.
You can still view questions and see answers without credits.
Submitting an answer counts as 1 attempt.
Seeing answer or explanation counts as a failed attempt.
Lastly, check your average score, across every attempt, in the top left.
MCQs are 1 point each. GQs are 1 point. FRQs will state points for each part.
Phy can give partial credit for GQs & FRQs.
Phy sees everything.
It customizes responses, explanations, and feedback based on what you struggle with. Try your best on every question!
Understand you mistakes quicker.
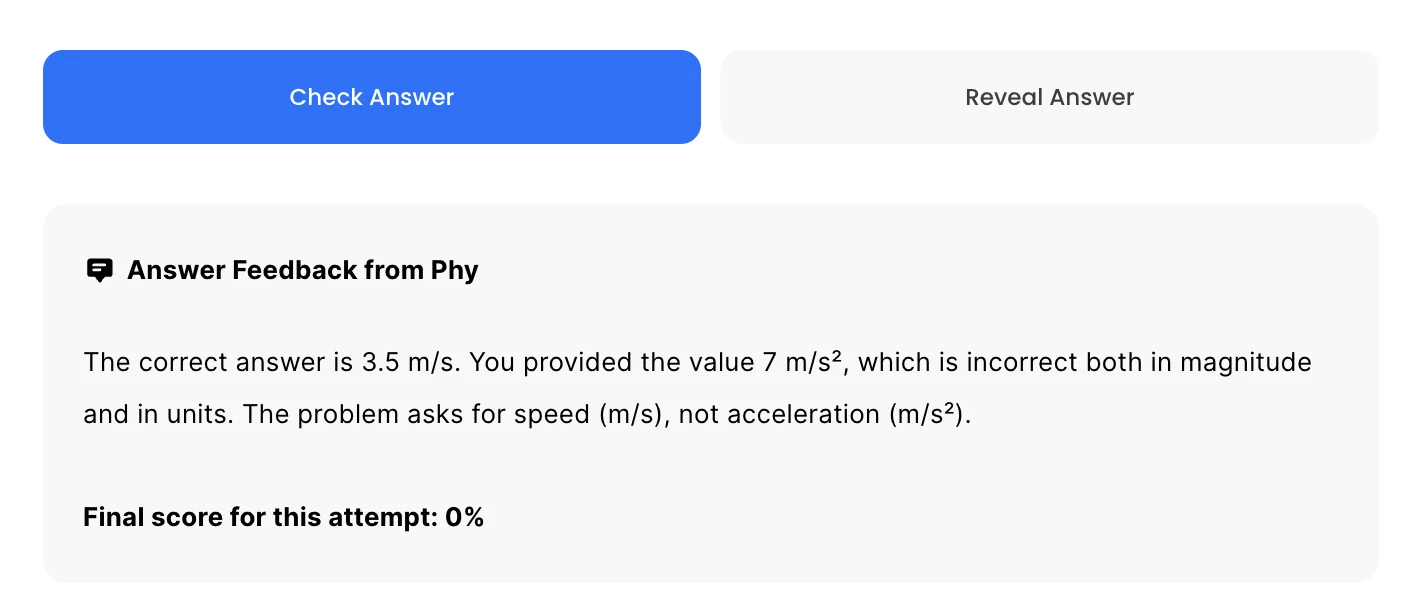
For GQs and FRQs, Phy provides brief feedback as to how you can improve your answer.
Aim to increase your understadning and average score with every attempt!
10 Free Credits To Get You Started
*Phy Pro members get unlimited credits
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.