A fisherman is standing in the back of his small fishing boat (the mass of the fisherman is the same as the mass of the boat) and he is a few meters from shore. He is done fishing so he starts walking towards the shore so he can get off the boat. What happens to the boat and the fisherman? Select all that apply and assume there is no friction between the boat and the water.
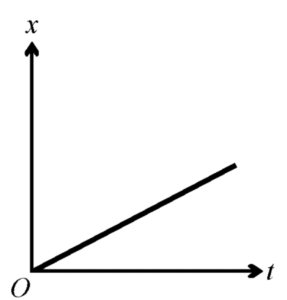 The displacement \(x\) of an object moving in one dimension is shown above as a function of time \(t\). The velocity of this object must be
The displacement \(x\) of an object moving in one dimension is shown above as a function of time \(t\). The velocity of this object must be
A rocket is fired at a speed of 75.0 m/s from ground level, at an angle of 60.0° above the horizontal. The rocket is fired toward an 11.0-m-high wall, which is located 27.0 m away. The rocket attains its launch speed in a negligibly short period of time, after which its engines shut down and the rocket coasts. By how much does the rocket clear the top of the wall?
You stand at the edge of a vertical cliff and throws a stone vertically upwards. The stone leaves your hand with a speed v = 8.0 m/s. The time between the stone leaving your hand and hitting the sea is 3.0 s. Assume air resistance is negligible. Calculate:
An elevator starts at rest on the ground floor. It accelerates upward smoothly for \( 2 \) \( \text{s} \) until reaching a steady upward speed. It continues at that constant speed for \( 5 \) \( \text{s} \) before gently slowing to rest at the next floor in \( 3 \) \( \text{s} \). Draw the velocity vs. time graph.
A block starts from rest at the top of a \(50^\circ\) incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is \(0.4\). If the block reaches a velocity of \(7 \, \text{m/s}\) at the bottom of the incline, what is the length of the incline?
In 2014, the European Space Agency placed a satellite in orbit around comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko and then landed a probe on the surface. The actual orbit was elliptical, but we can approximate it as a 50 km diameter circular orbit with a period of 11 days.
Can an object’s average velocity equal zero when object’s speed is greater than zero? Explain using the formula for average velocity vs speed.
A rocket explodes into two fragments, one \(25\) times heavier than the other. The change in momentum of the lighter fragment is
A fountain with an opening of radius \( 0.015 \) \( \text{m} \) shoots a stream of water vertically from ground level at \( 6.0 \) \( \text{m/s} \). The density of water is \( 1000 \) \( \text{kg/m}^3 \).
A spring launches a \(4 \, \text{kg}\) block across a frictionless horizontal surface. The block then ascends a \(30^\circ\) incline with a kinetic friction coefficient of \(\mu_k = 0.25\), stopping after \(55 \, \text{m}\) on the incline. If the spring constant is \(800 \, \text{N/m}\), find the initial compression of the spring. Disregard friction while in contact with the spring.
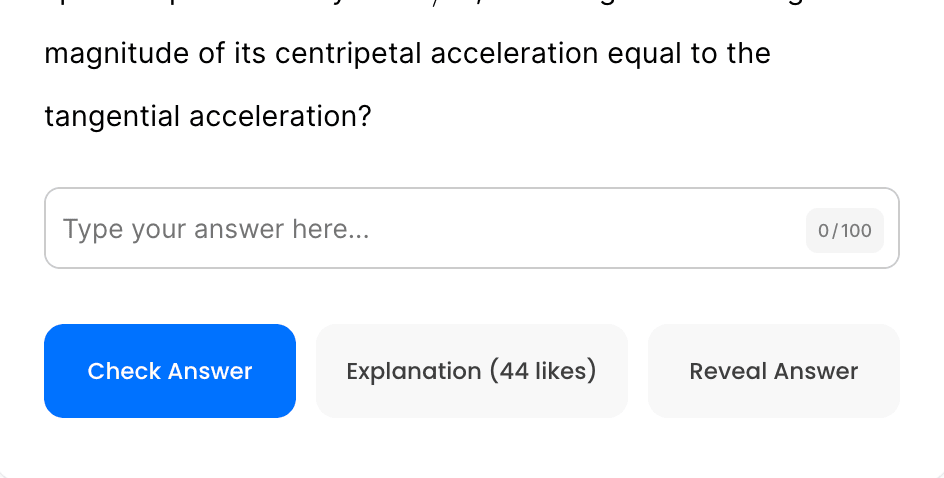
A new car is tested on a 230-m-diameter track. If the car speeds up at a steady [katex] 1.4 \, m/s^2[/katex], how long after starting is the magnitude of its centripetal acceleration equal to the tangential acceleration?
Find the approximate minimum mass needed for a spherical ball with a \(40\) \(\text{cm}\) radius to sink in a liquid of density \(1.4 \times 10^3\) \(\text{kg/m}^3\). Use \(9.8 \text{m/s}^2\) for \(g\).
The escape speed of an object of mass \( m \) from a planet of mass \( M \) and radius \( r \) depends on the gravitational constant and
A cart with an initial velocity of \(5.0 ~ \text{m/s}\)to the right experiences a constant acceleration of \(2.0 ~ \text{m/s}^2\) to the right. What is the cart’s displacement during the first \(6.0 ~ \text{s}\) of this motion?
Two blocks are on a horizontal, frictionless surface. Block \( A \) is moving with an initial velocity of \( v_0 \) toward block \( B \), which is stationary. The two blocks collide, stick together, and move off with a velocity of \( \frac{v_0}{3} \). Which block, if either, has the greater mass?
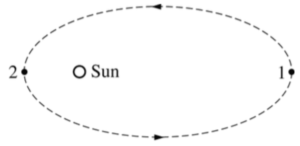
The elliptical orbit of a comet is shown above. Positions 1 and 2 are, respectively, the farthest and nearest positions to the Sun, and at position 1 the distance from the comet to the Sun is 10 times that at position 2. At position 2, the comet’s kinetic energy is
Two masses, \( m_1 \) and \( m_2 \), are suspended on either side of a pulley with a radius \( R \), as shown. The heavier mass, \( m_2 \), is initially held at rest above the ground by a distance \( h \) before being released. An student measures that it takes an amount of time \( t \) for the heavier mass to hit the ground after being released.
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.