Two uniform solid balls, one of radius \( R \) and mass \( M \), the other of radius \( 2R \) and mass \( 8M \), roll down a high incline. They start together from rest at the top of the incline. Which one will reach the bottom of the incline first?
A \( 25.0 \) \( \text{kg} \) block is placed at the top of an inclined plane set at an angle of \( 35 \) degrees to the horizontal. The block slides down the \( 1.5 \) \( \text{m} \) slope at a constant rate. How much work did friction do on the block?
A merry-go-round spins freely when Diego moves quickly to the center along a radius of the merry-go-round. As he does this, it is true to say that
How long does it take for a rotating object to speed up from 15.0 rad/s to 33.3 rad/s if it has a uniform angular acceleration of 3.45 rad/s2?
A spinning ice skater on extremely smooth ice is able to control the rate at which she rotates by pulling in her arms. Which of the following statements are true about the skater during this process?
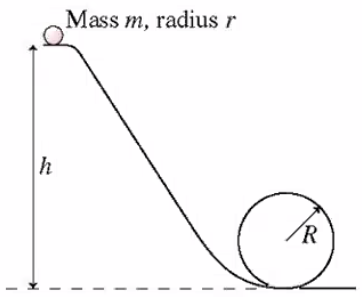
In the figure above, the marble rolls down the track and around a loop-the-loop of radius \( R \). The marble has mass \( m \) and radius \( r \). What minimum height \( h_{min} \) must the track have for the marble to make it around the loop-the-loop without falling off? Express your answer in terms of the variables \( R \) and \( r \).
The exoplanet HD 69830b has a mass 10 times that of the Earth and a radius 5 times that of the Earth. The value of g on HD 69830b is most nearly
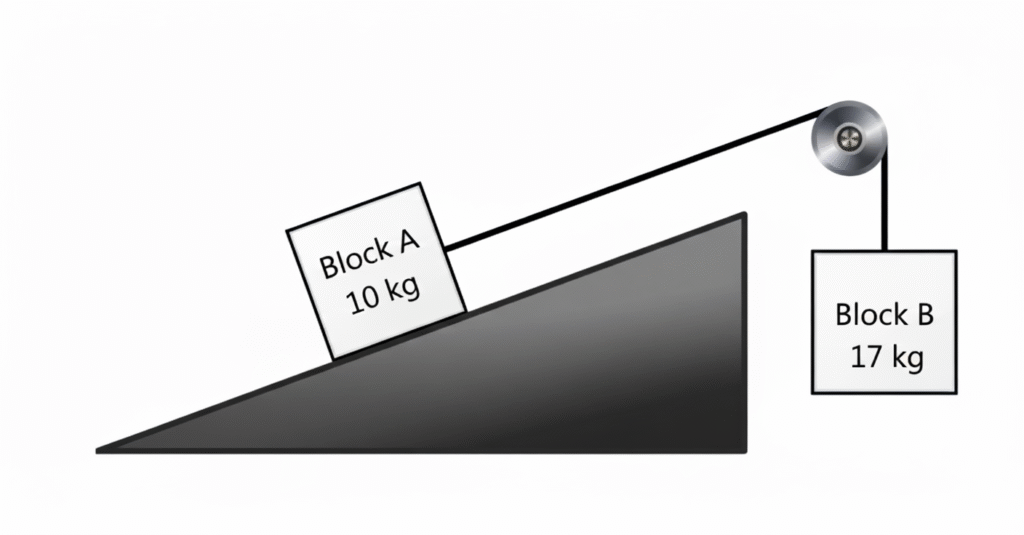
Two blocks, A and B, are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley. Block A, of mass \( 10 \) \( \text{kg} \), rests on a rough plane that makes an angle of \( 45^{\circ} \) with the horizontal, while block B, of mass \( 17 \) \( \text{kg} \), hangs vertically. Starting from rest, what is the minimum coefficient of static friction between block A and the plane required to keep the system in static equilibrium?
A rubber ball with a mass of \(0.25 \, \text{kg}\) and a speed of \(19.0 \, \text{m/s}\) collides perpendicularly with a wall and bounces off with a speed of \(21 \, \text{m/s}\) in the opposite direction. What is the magnitude of the impulse acting on the rubber ball?
A uniform ladder of length \(L\) and weight \(W = 50 \, \text{N}\) rests against a smooth vertical wall. If the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is \(\mu = 0.4\).
A net torque is applied to the edge of a spinning object as it rotates about its internal axis. The table shows the net torque exerted on the object at different instants in time. How can a student use the data table to determine the change in angular momentum of the object from \( 0 \) to \( 6 \) \( \text{s} \)? Justify your selection.
| Time \( (\text{s}) \) | Net Torque \( (\text{N} \cdot \text{m}) \) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1.5 |
| 4 | 3.0 |
| 6 | 4.5 |
A friend is balancing a fork on one finger. Which of the following are correct explanations of how he accomplishes this? Select two answers.

A horizontal tube with two vertical T-branches (A and B) is partially submerged in a liquid, with the open ends of the branches exposed to the air. However, the section of the tube above point B is hidden from view and may either be wider or narrower than the section above A.
Air is blown through the horizontal tube, causing the liquid levels in the vertical branches to rise as shown. Based on the observed water levels, which of the following best describes the characteristics of the hidden section of the tube above B?
A liquid flows at a constant flow rate through a pipe with circular cross-sections of varying diameters. At one point in the pipe, the diameter is \(2\) \(\text{cm}\) and the flow speed is \(18\) \(\text{m/s}\). What is the flow speed at another point in this pipe, where the diameter is \(3\) \(\text{cm}\).
A \(3300 \, \text{m}\)-high mountain is located on the equator. How much faster does a climber on top of the mountain move than a surfer at a nearby beach? The Earth’s radius is \(6400 \, \text{km}\) and the Earth’s mass is \(5.97 \times 10^{24} \, \text{kg}\).
One ball is dropped vertically from a window. At the same instant, a second ball is thrown horizontally from the same window. Which ball has the greater speed at ground level?
A space probe far from the Earth is travelling at \( 14.8 \) \( \text{km s}^{-1} \). It has mass \( 1\,312 \) \( \text{kg} \). The probe fires its rockets to give a constant thrust of \( 156 \) \( \text{kN} \) for \( 220. \) \( \text{s} \). It accelerates in the same direction as its initial velocity. In this time it burns \( 150. \) \( \text{kg} \) of fuel.
Calculate the final speed of the space probe in \( \text{km s}^{-1} \).
Which launch angle gives the greatest horizontal range, assuming level ground and no air resistance?
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.