Two blocks of ice, one five times as heavy as the other, are at rest on a frozen lake. A person then pushes each block the same distance \(d\). Ignore friction and assume that an equal force \(F\) is exerted on each block. Which of the following statements is true about the kinetic energy of the heavier block after the push?
Water at a gauge pressure of \( 3.8 \) \( \text{atm} \) at street level flows into an office building at a speed of \( 0.78 \) \( \text{m/s} \) through a pipe \( 5.0 \) \( \text{cm} \) in diameter. The pipe tapers down to \( 2.8 \) \( \text{cm} \) in diameter by the top floor, \( 16 \) \(\text{m} \) above, where the faucet has been left open. Calculate the flow velocity AND the gauge pressure in the pipe on the top floor. Assume no branch pipes and ignore viscosity.
Two students push a \(1750\, \mathrm{kg}\) car with a force of \(758\, \mathrm{N}\) along a perfectly level road at a constant velocity of \(4.00\, \mathrm{m/s}\). Find the force of friction.
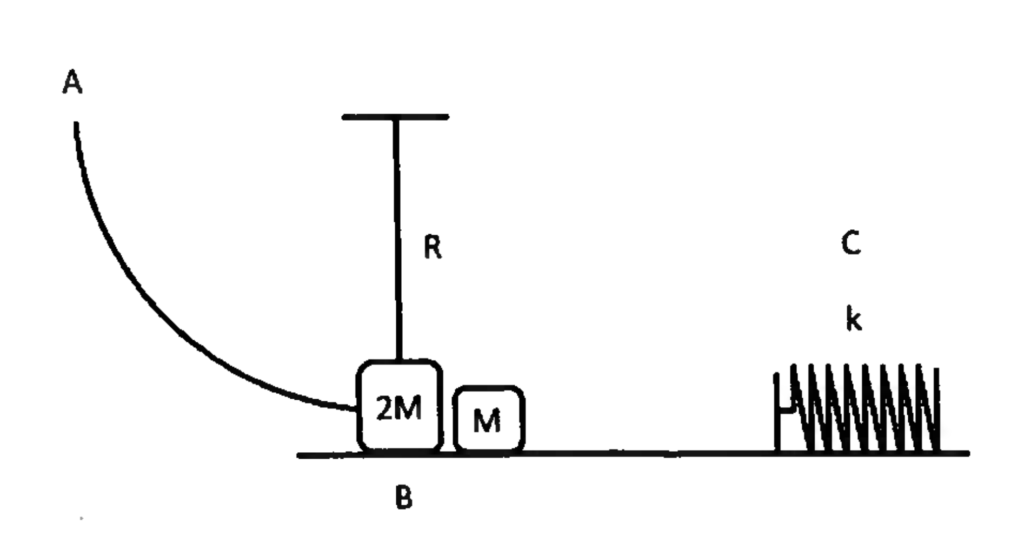
Refer to the diagram above and solve all equations in terms of \(R\), \(M\), \(k\), and constants.
A block starts at rest on a frictionless inclined track which then turns into a circular loop of radius \( R \) and is vertical. In terms of \( R \) and constants, find the minimum height \( h \) above the bottom of the loop the block must start from so it makes it around the loop.
A uniform ladder of length \(L\) and weight \(W = 50 \, \text{N}\) rests against a smooth vertical wall. If the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the ground is \(\mu = 0.4\).
A \(4.0 \, \text{kg}\) block is moving at \(5.0 \, \text{m/s}\) along a horizontal frictionless surface toward an ideal spring that is attached to a wall. After the block collides with the spring, the spring is compressed a maximum distance of \(0.68 \, \text{m}\). What is the speed of the block when the spring is compressed to only one-half of the maximum distance?
A solid sphere \( \left( I = \frac{2}{5}MR^2 \right) \) and a solid cylinder \( \left( I = \frac{1}{2}MR^2 \right) \), both uniform and of the same mass and radius, roll without slipping at the same forward speed. It is correct to say that the total kinetic energy of the solid sphere is
A 0.72-m-diameter solid sphere can be rotated about an axis through its center by a torque of 10.8 N·m which accelerates it uniformly from rest through a total of 160 revolutions in 15.0 s. What is the mass of the sphere?
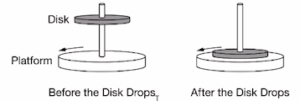
A platform is initially rotating on smooth ice with negligible friction, as shown above. A stationary disk is dropped directly onto the center of the platform. A short time later, the disk and platform rotate together at the same angular velocity, as shown at right in the figure. How does the angular momentum of only the platform change, if at all, after the disk drops? And what is the best justification.
Two blocks are on a horizontal, frictionless surface. Block \( A \) is moving with an initial velocity of \( v_0 \) toward block \( B \), which is stationary. The two blocks collide, stick together, and move off with a velocity of \( \frac{v_0}{3} \). Which block, if either, has the greater mass?
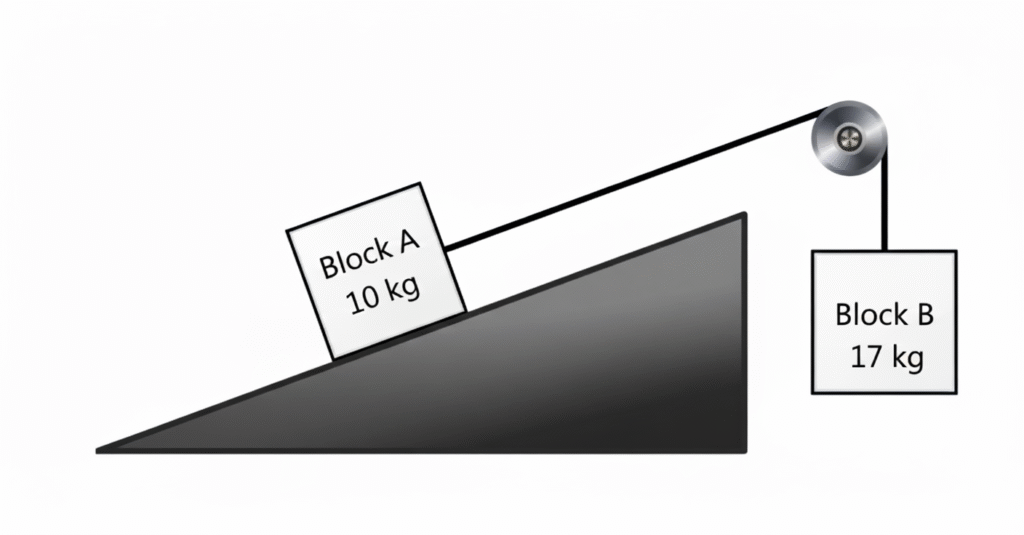
Two blocks, A and B, are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley. Block A, of mass \( 10 \) \( \text{kg} \), rests on a rough plane that makes an angle of \( 45^{\circ} \) with the horizontal, while block B, of mass \( 17 \) \( \text{kg} \), hangs vertically. Starting from rest, what is the minimum coefficient of static friction between block A and the plane required to keep the system in static equilibrium?
Water flowing in a horizontal pipe speeds up as it goes from a section with a large diameter to a section with a small diameter. Which of the following can explain why the speed of the water increases?
A red car, initially at rest, travels east with an acceleration of \( 3.5 \, \text{m/s}^2 \). At the same time as the red car starts to move, a blue car is traveling west at \( 15 \, \text{m/s} \) and accelerating at \( 1.2 \, \text{m/s}^2 \). If they are \( 600 \, \text{m} \) apart the moment the red car starts to move and they are traveling towards each other, where and when will they meet?
In \(3.0 \, \text{minutes}\), a ski lift raises \(10\) skiers at constant speed to a height of \(85 \, \text{m}\). The ski lift is \(55^\circ\) above the horizontal and the average mass of each skier is \(67.5 \, \text{kg}\). What is the average power provided by the tension in the cable pulling the lift?
A Christmas ornament made from a thin hollow glass sphere hangs from a thin wire of negligible mass. It is observed to oscillates with a frequency of \( 2.50 \) \( \text{Hz} \) in a city where \( g = 9.80 \) \( \text{m/s}^2 \). What is the radius of the ornament? The moment of inertia of the ornament is given by \( I = \frac{5}{3} mr^2 \).
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.