
Water flows from point \( A \) to points \( D \) and \( E \) as shown. Some of the flow parameters are known, as shown in the table. Determine the unknown parameters. Note the diagram above does not show the relative diameters of each section of the pipe.
| Section | Diameter | Flow Rate | Velocity |
|---|---|---|---|
| \( \text{AB} \) | \( 300 \) \( \text{mm} \) | \(\textbf{?}\) | \(\textbf{?}\) |
| \( \text{BC} \) | \( 600 \) \( \text{mm} \) | \(\textbf{?}\) | \( 1.2 \) \( \text{m/s} \) |
| \( \text{CD} \) | \(\textbf{?}\) | \( Q_{CD} = 2Q_{CE} \) \( \text{m}^3/\text{s} \) | \( 1.4 \) \( \text{m/s} \) |
| \( \text{CE} \) | \( 150 \) \( \text{mm} \) | \( Q_{CE} = 0.5Q_{CD} \) \( \text{m}^3/\text{s} \) | \(\textbf{?}\) |
A 250 newton centripetal force acts on a car moving at a constant speed in a horizontal circle. If the same force is applied, but the radius is made smaller, what happens to the speed v and the frequency f of the car?
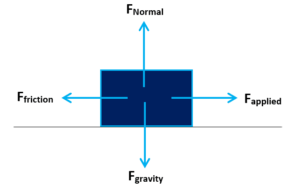
The box in the diagram is sliding to the right across a horizontal table, under the influence of the forces shown. Which force(s) is doing negative work on the box?
A pendulum consists of a mass \( M \) hanging at the bottom end of a massless rod of length \( \ell \) which has a frictionless pivot at its top end. A mass \( m \), moving with velocity \( v \), impacts \( M \) and becomes embedded. In terms of the given variables and constants, what is the smallest value of \( v \) sufficient to cause the pendulum (with embedded mass \( m \)) to swing clear over the top of its arc?
The angular velocity of an electric motor is \(\omega = \left(20 – \frac{1}{2} t^2 \right) \, \text{rad/s}\), where \(t\) is in seconds.
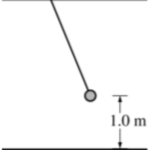
A 0.5 kg pendulum bob is raised to 1.0 m above the floor, as shown in the figure. The bob is then released from rest. When the bob is 0.8 m above the floor, its speed is most nearly
A turntable rotates through \( 6 \) \( \text{rad} \) in \( 3 \) \( \text{s} \) as it accelerates uniformly from rest. What is its angular acceleration in \( \text{rad/s}^2 \)?
To increase the moment of inertia of a body about an axis, you must
Two students are on a balcony 19.6 m above the street. One student throws a ball vertically downward at 14.7 m/s. At the same instant, the other student throws a ball vertically upward at the same speed. The second ball just misses the balcony on the way down.
A block of mass [katex] m [/katex] is moving on a horizontal frictionless surface with a speed [katex] v_0 [/katex] as it approaches a block of mass [katex] 2m [/katex] which is at rest and has an ideal spring attached to one side.
When the two blocks collide, the spring is completely compressed and the two blocks momentarily move at the same speed, and then separate again, each continuing to move.
A pair of fuzzy dice is hanging by a string from your rearview mirror. You speed up from a stoplight. During the acceleration, the dice do not move vertically; the string makes an angle of \( 22^\circ \) with the vertical. The dice have a mass of \( 0.10 \, \text{kg} \). Determine the acceleration.
A windmill blade with a rotational inertia of \( 6.0 \) \( \text{kg} \cdot \text{m}^2 \) has an initial angular velocity of \( 8 \) \( \text{rad/s} \) in the clockwise direction. It is then given an angular acceleration of \( 4 \) \( \text{rad/s}^2 \) in the clockwise direction for \( 10 \) seconds. What is the change in rotational kinetic energy of the blade over this time interval?
Determine the force needed to push a \( 150 \) \( \text{kg} \) body up a smooth \( 30^\circ \) incline with an acceleration of \( 6 \) \( \text{m/s}^2 \).
A person shoots a basketball with a speed of \( 12 \, \text{m/s} \) at an angle of \( 35^\circ \) above the horizontal. If the person is \( 2.4 \, \text{m} \) tall and the hoop is \( 3.05 \, \text{m} \) above the ground, how far back must the person stand in order to make the shot?
A rocket, initially at rest, is fired vertically upward with an acceleration of \( 12.0 \, \text{m/s}^2 \). At an altitude of \( 1.00 \, \text{km} \), the rocket engine cuts off. Drag is negligible.
A boat can row across a still \( 1 \, \text{km} \) wide river at a maximum speed of \( 5 \, \text{km/hr} \). If a current of \( 4 \, \text{km/hr} \) flows east as you try to directly cross the river, how long would it take?
A \(1.5 \, \text{kg}\) object is located at a distance of \(1.7 \times 10^{6} \, \text{m}\) from the center of a larger object whose mass is \(7.4 \times 10^{22} \, \text{kg}\).
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.