A stone is falling at a constant velocity vertically down a tube filled with oil. Which of the following statements about the energy changes of the stone during its motion are correct?
I. The gain in kinetic energy is less than the loss in gravitational potential energy.
II. The sum of kinetic and gravitational potential energy of the stone is constant.
III. The work done by the force of gravity has the same magnitude as the work done by friction.
A disk increases from 2 complete revolutions in 2 seconds to 5 complete revolutions in 2 seconds. What is its average angular acceleration?
Two students are on a balcony 19.6 m above the street. One student throws a ball vertically downward at 14.7 m/s. At the same instant, the other student throws a ball vertically upward at the same speed. The second ball just misses the balcony on the way down.
A block sliding down an frictionless inclined plane is experiencing both gravitational and normal forces; which force’s magnitude changes when the angle of the incline is increased?
A typical \( 68 \text{-kg} \) person generates a steady mechanical power output of \( 120 \text{ W} \) at the pedals of a bicycle. Approximately how many Calories are “burned” (total metabolic energy expended) when the person rides a bicycle for \( 15 \text{ minutes} \)? A typical energy efficiency for the human body is \( 25\% \), which takes into account the release of thermal energy. Note (\( 1 \text{ Cal} = 4186 \text{ J} \)).
Four systems are in rotational motion. Which of the following combinations of rotational inertia and angular speed for each of the systems corresponds to the greatest rotational kinetic energy?
| System | Rotational Inertia | Angular Speed |
|---|---|---|
| A | \( I_0 \) | \( \omega_0 \) |
| B | \( I_0 \) | \( 4\, \omega_0 \) |
| C | \( 2 I_0 \) | \( 2\, \omega_0 \) |
| D | \( 6 I_0 \) | \( \omega_0 \) |
Two uniform disks have the same mass but different radii: disk \( 1 \) has a radius \( R \) and disk \( 2 \) has a radius \( 2R \). What is the ratio of the moment of inertia of the first disk to the second disk?
A diver springs upward from a diving board. At the instant she contacts the water, her speed is \( 8.90 \, \text{m/s} \), and her body is extended at an angle of \( 75.0^\circ \) with respect to the horizontal surface of the water. At this instant, her vertical displacement is \( -3.00 \, \text{m} \), where downward is the negative direction. Determine her initial velocity, both magnitude and direction.
A block is attached to a horizontal spring. The block is held so the spring is stretched and the block is released from rest, undergoing simple harmonic motion with a frequency of \( 2 \) \( \text{Hz} \). How long after release will the block first reach a point where it is momentarily at rest?
A solid sphere, solid cylinder, and a hollow pipe all have equal masses and radii. If the three of them are released simultaneously at the top of an inclined plane and do not slip, which one will reach the bottom first? [katex] I_{sphere} = \frac{2}{5}MR^2[/katex], [katex] I_{cylinder} = \frac{1}{2}MR^2[/katex], [katex] I_{pipe} = MR^2[/katex]
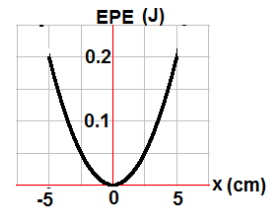
A 0.4 kg object is attached to a horizontal spring undergoes SHM with the total energy of 0.2 J. The potential energy as a function of position presented by the graph.
A solid ball and a cylinder roll down an inclined plane. Which reaches the bottom first? Hint the rotational inertia of a sphere about its center is \(I = \frac{2}{5}mR^{2}\) and the rotational inertia of a cylinder about its center is \(I = \frac{1}{2}mR^{2}\).
A \(2 \, \text{kg}\) object slides east at \(4 \, \text{m/s}\) and collides with a stationary \(3 \, \text{kg}\) object. After the collision, the \(2 \, \text{kg}\) object is traveling at an unknown velocity at \(15^\circ\) north of east and the \(3 \, \text{kg}\) object is traveling at \(38^\circ\) south of east. What is each object’s final velocity?
What is the mass of a dog that weighs \(58 \, \text{N}\) on Earth?
A rotating merry-go-round makes one complete revolution in 4.0 s. What is the linear speed and acceleration of a child seated 1.2 m from the center?
Two balls are launched at the same speed. Ball A is launched at an angle of \( 45^{\circ} \) and Ball B is launched at an angle of \( 60^{\circ} \). Which one reaches a higher point?
Consider a solid uniform sphere of radius \(R\) and mass \(M\) rolling without slipping. Which form of its kinetic energy is larger, translational or rotational?
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.