for free to use all UBQ features
Three blocks are stacked on top of one another. The top block has a mass of \( 4.6 \, \text{kg} \), the middle one has a mass of \( 1.2 \, \text{kg} \), and the bottom one has a mass of \( 3.7 \, \text{kg} \).
Identify and calculate any normal forces between the objects.
A 1.0-kg object is moving with a velocity of 6.0 m/s to the right. It collides and sticks to a 2.0-kg object moving with a velocity of 3.0 m/s in the same direction. How much kinetic energy was lost in the collision?
An object is thrown upward at \( 65 \, \text{m/s} \) from the top of a \( 800 \, \text{m} \) tall building.
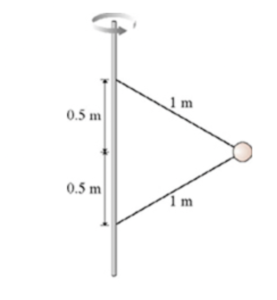
Two wires are tied to the \(500 \, \text{g}\) sphere as shown above. The sphere revolves in a horizontal circle at a constant speed of \(7.2 \, \text{m/s}\). What is the tension in the upper wire? What is the tension in the lower wire?
A \( 25.0 \) \( \text{kg} \) block is placed at the top of an inclined plane set at an angle of \( 35 \) degrees to the horizontal. The block slides down the \( 1.5 \) \( \text{m} \) slope at a constant rate. How much work did friction do on the block?

A massless rigid rod of length [katex]3d[/katex] is pivoted at a fixed point [katex]W[/katex], and two forces each of magnitude [katex]F[/katex] are applied vertically upward as shown above. A third vertical force of magnitude [katex]F[/katex] may be applied, either upward or downward, at one of the labeled points. With the proper choice of direction at each point, the rod can be in equilibrium if the third force of magnitude [katex]F[/katex] is applied at point?
A spring launches a \(4 \, \text{kg}\) block across a frictionless horizontal surface. The block then ascends a \(30^\circ\) incline with a kinetic friction coefficient of \(\mu_k = 0.25\), stopping after \(55 \, \text{m}\) on the incline. If the spring constant is \(800 \, \text{N/m}\), find the initial compression of the spring. Disregard friction while in contact with the spring.
Traveling at a speed of 15.9 m/s, the driver of an automobile suddenly locks the wheels by slamming on the brakes. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the road is 0.659. What is the speed of the automobile after 1.59 s have elapsed? Ignore the effects of air resistance.
If I weigh \( 741 \) \( \text{N} \) on Earth at a place where \( g = 9.80 \) \( \text{m/s}^2 \) and \( 5320 \) \( \text{N} \) on the surface of another planet, what is the acceleration due to gravity on that planet?
A mechanic pushes a [katex]2500 \, \text{kg}[/katex] car from rest to a final speed [katex]v[/katex] by doing [katex]5.0 \times 10^3 \, \text{J}[/katex] of work on the car. Frictional effect between the car and the ground are negligible. What is the final speed of the car?
Two identical metal balls are being held side by side at the top of a ramp. Alex lets one ball, \( A \), start rolling down the hill. A few seconds later, Alex’s partner, Bob, starts the second ball, \( B \), down the hill by giving it a push. Ball \( B \) rolls down the hill along a line parallel to the path of the first ball and passes it. At the instant ball \( B \) passes ball \( A \):
If a small motor does 520 J of work to move a toy car 260 meters in a time of 37 seconds.
Riders in a carnival ride stand with their backs against the wall of a circular room of diameter \(8.0 \, \text{m}\). The room is spinning horizontally about an axis through its center at a rate of \(45 \, \text{rev/min}\) when the floor drops so that it no longer provides any support for the riders. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rider required so that the rider does not slide down the wall?
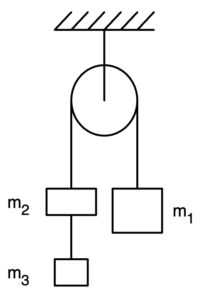
Three blocks of masses \(m_3 = 1.0 \, \text{kg}\), \(m_2 = 2.0 \, \text{kg}\), and \(m_1 = 4.0 \, \text{kg}\) are connected by massless strings, one of which passes over a frictionless pulley of negligible mass, as shown above.
A proton (mp = 1.67 x10-27 kg) is being accelerated along a straight line at 3.6 ×1015 m/s2 in a machine. The proton has an initial speed of 2.4 x107 m/s and travels 3.5 cm.
A baseball, mass \(0.5 \, \text{kg}\), is traveling to the right at \(32.2 \, \text{m/s}\) when it is hit by a bat and travels the opposite direction at \(72.2 \, \text{m/s}\). The bat hits the ball with a force of \(1,222 \, \text{N}\). What is the ball’s change in momentum and how long was the ball in contact with the bat?
A 100-pound rock and a 1-pound metal arrow pointed downwards are dropped from height \( h \). Assuming there is no air resistance, which one hits the ground first and why?
A box is sliding down an incline at a constant speed of \( 2 \, \text{m/s} \). The angle of the incline is \( \theta \). The magnitude of the total of the opposing forces is \( 16 \, \text{N} \). Derive an equation for the force of gravity acting on the box.
Caleb is filling up water balloons for the Physics Olympics balloon toss competition. Caleb sets a \( 0.50 \text{-kg} \) spherical water balloon on the kitchen table and notices that the bottom of the balloon flattens until the pressure on the bottom is reduced to \( 630 \frac{\text{N}}{\text{m}^2} \). What is the area of the flat spot on the bottom of the balloon?
An airplane can safely bank when subjected to a centripetal acceleration of 8 g’s. If the airplane flies at a constant speed of 400 m/s, how long does it take to make a 180° turn?
An object’s angular momentum changes by \( 10 \,\text{kg} \cdot \text{m}^2/\text{s} \) in \( 2.0 \) \( \text{s} \). What magnitude average torque acted on this object?
A group of astronauts in a spaceship are attempting to land on Mars. As they approach the planet, they begin to plan their descent to the surface.
A solid ball and a cylinder roll down an inclined plane. Which reaches the bottom first? Hint the rotational inertia of a sphere about its center is \(I = \frac{2}{5}mR^{2}\) and the rotational inertia of a cylinder about its center is \(I = \frac{1}{2}mR^{2}\).
A race car traveling at a constant speed of \( 50 \) \( \text{m/s} \) drives around a circular track that is \( 500 \) \( \text{m} \) in diameter. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the car?
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.