Police officers have measured the length of a car’s tire skid marks to be \( 23 \, \text{m} \). This particular car is known to decelerate at a constant \( 7.5 \, \text{m/s}^2 \). What was the car’s initial velocity?
Initially, a ball has an angular velocity of \( 5.0 \) \( \text{rad/s} \) counterclockwise. Some time later, after rotating through a total angle of \( 5.5 \) \( \text{radians} \), the ball has an angular velocity of \( 1.5 \) \( \text{rad/s} \) clockwise.
A pulley system consists of two blocks of mass \( 5 \) \( \text{kg} \) and \( 10 \) \( \text{kg} \), connected by a rope of negligible mass that passes over a pulley of radius \( 0.1 \) \( \text{m} \) and mass \( 2 \) \( \text{kg} \). The pulley is free to rotate about its axis. The system is released from rest, and the block of mass \( 10 \) \( \text{kg} \) starts to move downwards. Assume the pulley has a frictional force of \(5.7\) Newtons acting on the outer edge of the pulley.
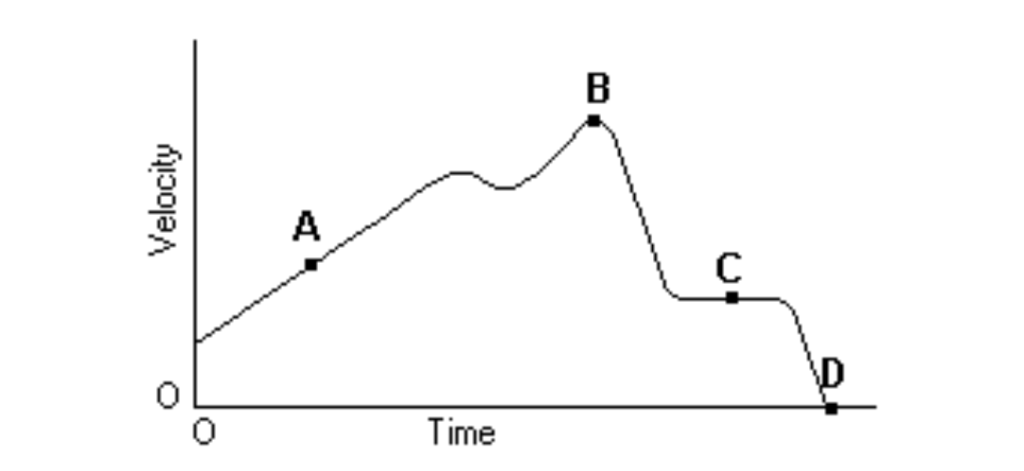 Above is the graph of the velocity vs. time of a duck flying due south for the winter. At what point might the duck begin reversing directions?
Above is the graph of the velocity vs. time of a duck flying due south for the winter. At what point might the duck begin reversing directions?
An object is moving in a horizontal circle at a constant speed. Which of the following correctly describes the linear and angular velocities of the object between any point along the circular path?
A car moves forward at a steady \( 10 \) \( \text{m/s} \) for \( 5 \) \( \text{s} \). The driver slams the brakes and brings it to rest in \( 2 \) \( \text{s} \). Without waiting, the driver immediately accelerates backward (negative velocity) for \( 3 \) \( \text{s} \) until reaching \( 8 \) \( \text{m/s} \) in reverse. Draw the velocity vs. time graph.
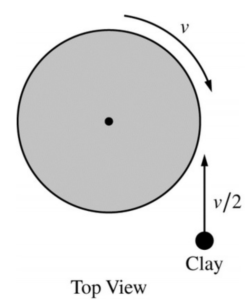
A system consists of a disk rotating on a frictionless axle and a piece of clay moving toward it, as shown in the figure above. The outside edge of the disk is moving at a linear speed \( v \), and the clay is moving at speed \( \frac{v}{2} \). The clay sticks to the outside edge of the disk. How does the angular momentum of the system after the clay sticks compare to the angular momentum of the system before the clay sticks, and what is an explanation for the comparison?
An object of unknown mass is acted upon by multiple forces:
The coefficients of friction are \(\mu_s = 0.6\) and \(\mu_k = 0.2\). Starting from rest, the object travels \(10 \, \text{m}\) in \(4.5 \, \text{s}\). What is the mass of the unknown object?
A 6.0-cm-diameter gear rotates with angular velocity \( \omega = \left(20-\frac {1}{2} t^2 \right) \, \text {rad/s} \), where \(t\) is in seconds. At \(t = 4.0 \, \text{s}\), what are
A theme park ride consists of a large vertical wheel of radius \( R \) that rotates counterclockwise on a horizontal axle through its center. The cars on the wheel move at a constant speed \( v \). Points \( A \) and \( D \) represent the position of a car at the highest and lowest point of the ride, respectively. While passing point \( A \), a student releases a small rock of mass \( m \), which falls to the ground without hitting anything. Which of the following best represents the kinetic energy of the rock when it is at the same height as point \( D \)?
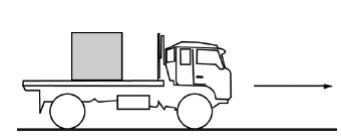
A \( 4700 \, \text{kg} \) truck carrying a \( 900 \, \text{kg} \) crate is traveling at \( 25 \, \text{m/s} \) to the right along a straight, level highway, as shown above. The truck driver then applies the brakes, and as it slows down, the truck travels \( 55 \, \text{m} \) in the next \( 3.0 \, \text{s} \). The crate does not slide on the back of the truck.
During lunch, Alex and Jordan argue about inertia. Alex says if she spins a basketball faster, it will have greater inertia. Jordan argues that inertia only depends on the ball’s mass, not its speed. Who is correct?
Consider a ball thrown up from the surface of the earth into the air at an angle of \( 30^\circ \) above the horizontal. Air resistance is negligible. The ball’s acceleration just after release is most nearly
A car’s velocity increases as follows each second: \( 2 \) \( \text{m/s} \), \( 4 \) \( \text{m/s} \), \( 6 \) \( \text{m/s} \), \( 8 \) \( \text{m/s} \). This pattern shows that the car is:
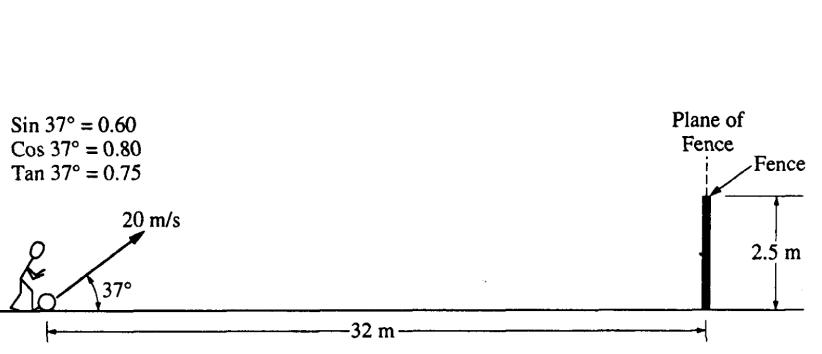
A ball of mass \( 0.5 \, \text{kg} \), initially at rest, is kicked directly toward a fence from a point \( 32 \, \text{m} \) away, as shown above. The velocity of the ball as it leaves the kicker’s foot is \( 20 \, \text{m/s} \) at an angle of \( 37^\circ \) above the horizontal. The top of the fence is \( 2.5 \, \text{m} \) high. The ball hits nothing while in flight and air resistance is negligible.
An object weighs \( 432 \) \( \text{N} \) on the surface of Earth. At a height of \( 3R_{\text{Earth}} \) above Earth’s surface, what is its weight?
A linear spring of force constant \( k \) is used in a physics lab experiment. A block of mass \( m \) is attached to the spring and the resulting frequency, \( f \), of the simple harmonic oscillations is measured. Blocks of various masses are used in different trials, and in each case, the corresponding frequency is measured and recorded. If \( f^{2} \) is plotted versus \( \frac{1}{m} \), the graph will be a straight line with slope
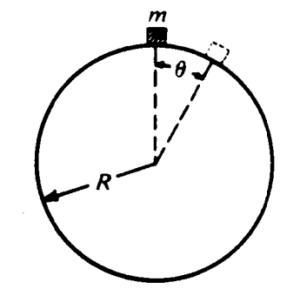
A particle of mass \(m\) slides down a fixed, frictionless sphere of radius \(R\), starting from rest at the top.
In terms of \(m\), \(g\), \(R\), and \(\theta\), determine each of the following for the particle while it is sliding on the sphere.
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.