Water flowing in a horizontal pipe speeds up as it goes from a section with a large diameter to a section with a small diameter. Which of the following can explain why the speed of the water increases?
A car accelerates from rest with an acceleration of \( 3.5 \, \text{m/s}^2 \) for \( 10 \, \text{s} \). After this, it continues at a constant speed for an unknown amount of time. The driver notices a ramp \( 50 \, \text{m} \) ahead and takes \( 0.6 \, \text{s} \) to react. After reacting, the driver hits the brakes, which slow the car with an acceleration of \( 7.2 \, \text{m/s}^2 \). Unfortunately, the driver does not stop in time and goes off the \( 3 \, \text{m} \) high ramp that is angled at \( 27^\circ \).

A block of mass \( 0.5 \) \( \text{kg} \) is attached to a horizontal spring with a spring constant of \( 150 \) \( \text{N/m} \). The block is released from rest at position \( x = 0.05 \) \( \text{m} \), as shown, and undergoes simple harmonic motion, reaching a maximum position of \( x = 0.1 \) \( \text{m} \). The speed of the block when it passes through position \( x = 0.09 \) \( \text{m} \) is most nearly
A comet of mass \( m_c = 3.2 \times 10^{14} \) \( \text{kg} \) is orbiting a star with mass \( m_s = 1.8 \times 10^{30} \) \( \text{kg} \). The comet’s orbit is elliptical. At its closest point, the comet is a distance \( r_1 = 8.3 \times 10^{10} \) \( \text{m} \) from the star, and at its farthest point, the comet is a distance \( r_2 = 4.9 \times 10^{11} \) \( \text{m} \) from the star. What is the change in the kinetic energy of the comet as it moves along its orbit from distance \( r_2 \) to distance \( r_1 \) from the star?
The moment of inertia of a solid cylinder about its axis is given by \( 0.5MR^2 \). If this cylinder rolls without slipping, the ratio of its rotational kinetic energy to its translational kinetic energy is
A person holds a book at rest a few feet above a table. The person then lowers the book at a slow constant speed and places it on the table. Which of the following accurately describes the change in the total mechanical energy of the Earth–book system?
A \(25 \, \text{g}\) steel ball is attached to the top of a \(24 \, \text{cm}\)-diameter vertical wheel of negligible mass. Starting from rest, the wheel accelerates at \(470 \, \text{rad/s}^2\). The ball is released after \(\frac{3}{4}\) of a revolution. How high does it go above the center of the wheel?
Caleb is filling up water balloons for the Physics Olympics balloon toss competition. Caleb sets a \( 0.50 \text{-kg} \) spherical water balloon on the kitchen table and notices that the bottom of the balloon flattens until the pressure on the bottom is reduced to \( 630 \frac{\text{N}}{\text{m}^2} \). What is the area of the flat spot on the bottom of the balloon?

A simple pendulum oscillates with amplitude \(A\) and period \(T\), as represented on the graph above. Which option best represents the magnitude of the pendulum’s velocity \(v\) and acceleration \(a\) at time \(\frac{T}{2}\)?
Which of the following graphs represent an object having zero acceleration?
A \(3300 \, \text{m}\)-high mountain is located on the equator. How much faster does a climber on top of the mountain move than a surfer at a nearby beach? The Earth’s radius is \(6400 \, \text{km}\) and the Earth’s mass is \(5.97 \times 10^{24} \, \text{kg}\).
Why do pilots sometimes black out while pulling out at the bottom of a dive?
A car moves forward at a steady \( 10 \) \( \text{m/s} \) for \( 5 \) \( \text{s} \). The driver slams the brakes and brings it to rest in \( 2 \) \( \text{s} \). Without waiting, the driver immediately accelerates backward (negative velocity) for \( 3 \) \( \text{s} \) until reaching \( 8 \) \( \text{m/s} \) in reverse. Draw the velocity vs. time graph.
When the speed of a rear-drive car is increasing on a horizontal road, what is the direction of the frictional force on the tires?
Two objects (49.0 and 24.0 kg) are connected by a massless string that passes over a massless, frictionless pulley. The pulley hangs from the ceiling. Find the acceleration of the objects and the tension in the string.
Which pulls harder gravitationally, the Earth on the Moon, or the Moon on the Earth? Which accelerates more?
An object is experiencing a nonzero net force. Which of the following statements is most accurate?
If a constant net torque is applied to an object it will (select all that applies):
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.
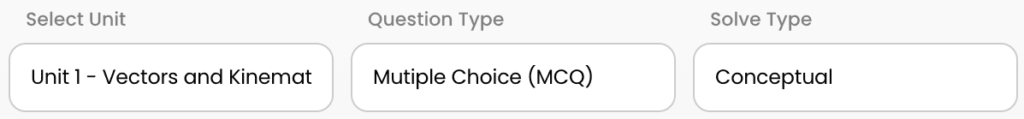

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

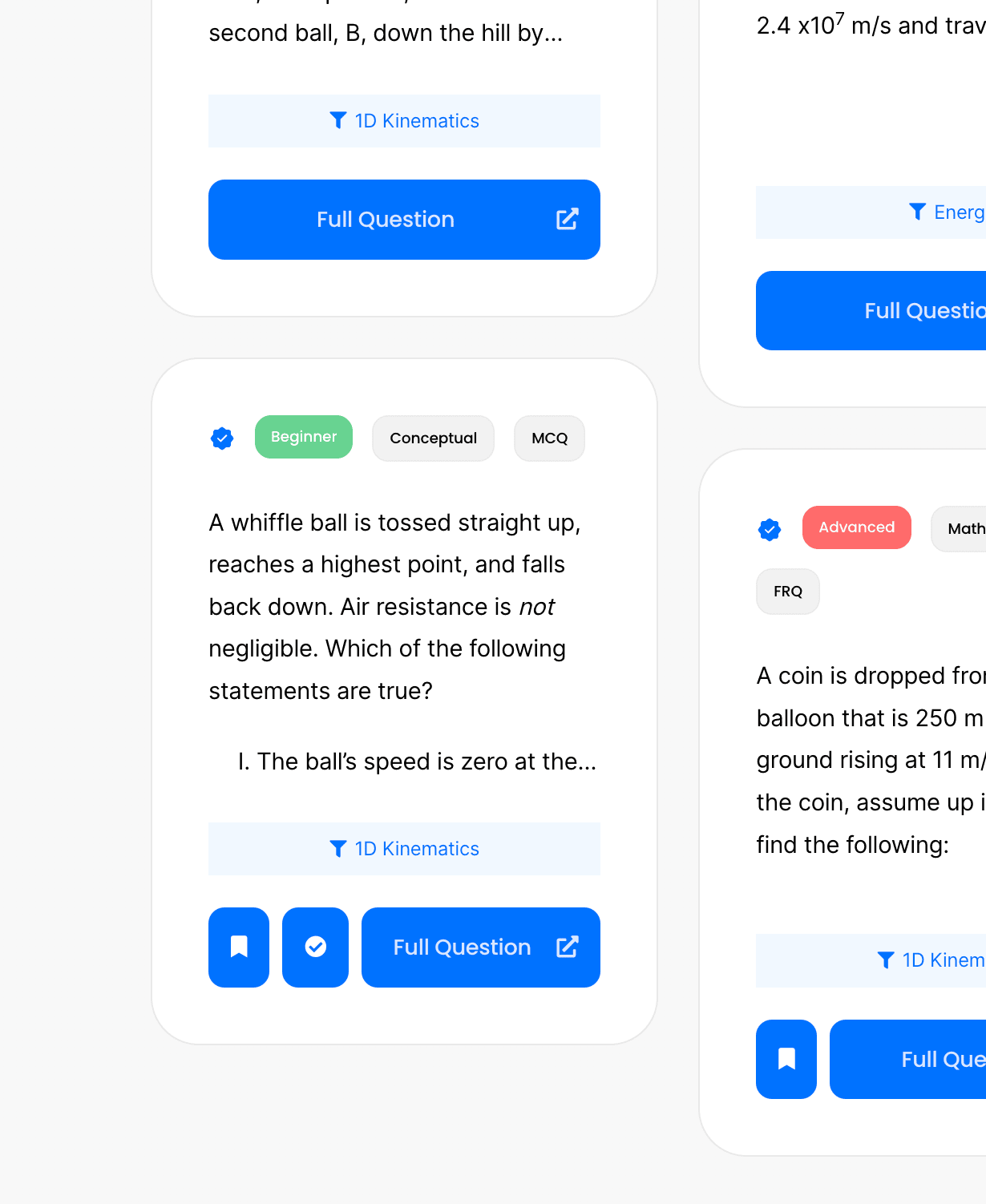
Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
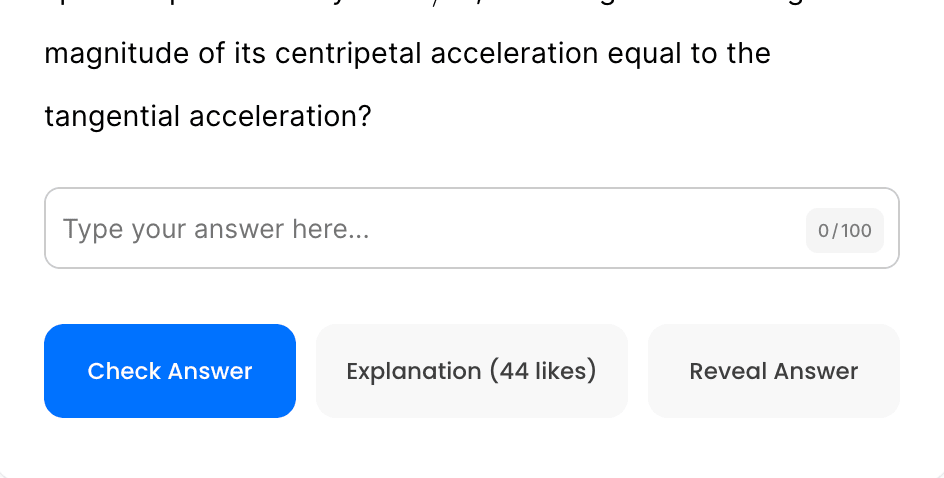
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.