A student walks \( 3 \) \( \text{m} \) east, then \( 4 \) \( \text{m} \) west in \( 7 \) \( \text{s} \). What is their displacement and average velocity?

The drawing above shows a spherical reservoir that contains \( 455,000 \) \( \text{kg} \) of water when full. The reservoir is vented to the atmosphere at the top. Assuming the reservoir is full and the diameter of the reservoir is much larger than any of the pipes on the ground.
A theme park ride consists of a large vertical wheel of radius \( R \) that rotates counterclockwise on a horizontal axle through its center. The cars on the wheel move at a constant speed \( v \). Points \( A \) and \( D \) represent the position of a car at the highest and lowest point of the ride, respectively. While passing point \( A \), a student releases a small rock of mass \( m \), which falls to the ground without hitting anything. Which of the following best represents the kinetic energy of the rock when it is at the same height as point \( D \)?
A pair of fuzzy dice is hanging by a string from your rearview mirror. You speed up from a stoplight. During the acceleration, the dice do not move vertically; the string makes an angle of \( 22^\circ \) with the vertical. The dice have a mass of \( 0.10 \, \text{kg} \). Determine the acceleration.
Which of the following must be zero if an object is spinning at a constant rate? There may be more than one right answer.
A rotating merry-go-round makes one complete revolution in 4.0 s. What is the linear speed and acceleration of a child seated 1.2 m from the center?
A rock is dropped from the top of a tall tower. Half a second later another rock, twice as massive as the first, is dropped. Ignoring air resistance and using ONLY simple kinematics (DO NOT use energy to explain this). Explain it like you would to a 5th grader and select the correct choice:
A sphere of mass \( M \) and radius \( r \), and rotational inertia \( I \) is released from the top of an inclined plane of height \( h \). The surface has considerable friction. Using only the variables mentioned, derive an expression for the sphere’s center of mass velocity.
A ball is thrown straight up. What are the velocity and acceleration of the ball at the highest point in its path?
A golfer hits a shot to a green that is elevated \(2.80 \, \text{m}\) above the point where the ball is struck. The ball leaves the club at a speed of \(18.9 \, \text{m/s}\) at an angle of \(52.0^\circ\) above the horizontal. It rises to its maximum height and then falls down to the green. Ignoring air resistance, find the speed of the ball just before it lands.
An object weighs \( 300 \, \text{N} \) on Earth and \( 50 \, \text{N} \) on the Moon. Does the object have less inertia on the Moon?

Which statement is true about the distances the two objects have traveled at time \( t_f \)?
A [katex] 2 \, \text{kg}[/katex] mass is attached to a spring with spring constant [katex] k = 100 \, \text{N/m}[/katex] and negligible mass.
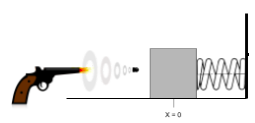
A bullet (mass: \(0.05 \, \text{kg}\)) is fired horizontally (\(v = 200 \, \text{m/s}\)) at a block (mass: \(1.3 \, \text{kg}\)) initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The block is attached to a spring (\(k = 2500 \, \text{N/m}\)). The bullet becomes embedded. Calculate:
A ball is dropped from the top of a tall building. At the same instant, a second ball is thrown upward from the ground level. When the two balls pass one another, one on the way up, the other on the way down, compare the magnitudes of their acceleration:
A ball rolls down a ramp and gains speed. Its velocity is increasing in the negative direction. What can be said about its acceleration?
A \(6 \, \text{kg}\) cube rests against a compressed spring with a force constant of \(1{,}800 \, \text{N/m}\), initially compressed by \(0.3 \, \text{m}\). Upon release, the cube slides on a horizontal surface with a kinetic friction coefficient of \(\mu_k = 0.12\) for \(3 \, \text{m}\), then ascends a \(12^\circ\) slope, stopping after \(4.5 \, \text{m}\). Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction on the slope.

Projectiles 1 and 2 are launched from level ground at the same time and follow the trajectories shown in the figure. Which one of the projectiles, if either, returns to the ground first, and why?
By continuing you (1) agree to our Terms of Use and Terms of Sale and (2) consent to sharing your IP and browser information used by this site’s security protocols as outlined in our Privacy Policy.
Quick Start Guide
AP physics 1, AP C, honors and advanced physics students.
Quickly filter questions by units and more.

Here’s guide to using 5 UBQ filters.
GQ = general question, MCQ = multiple choice, FRQ = free response.

Click the check or bookmark button.
Now you’ll be able to see completed or bookmarked questions at a glance!
Answer keys, personalized for you.
Phy will be responsible for grading your FRQs and GQs.
No more copy and pasting. Just solve and snap.
Questions for Mastery
By continuing you agree to nerd-notes.com Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and our usage of user data.